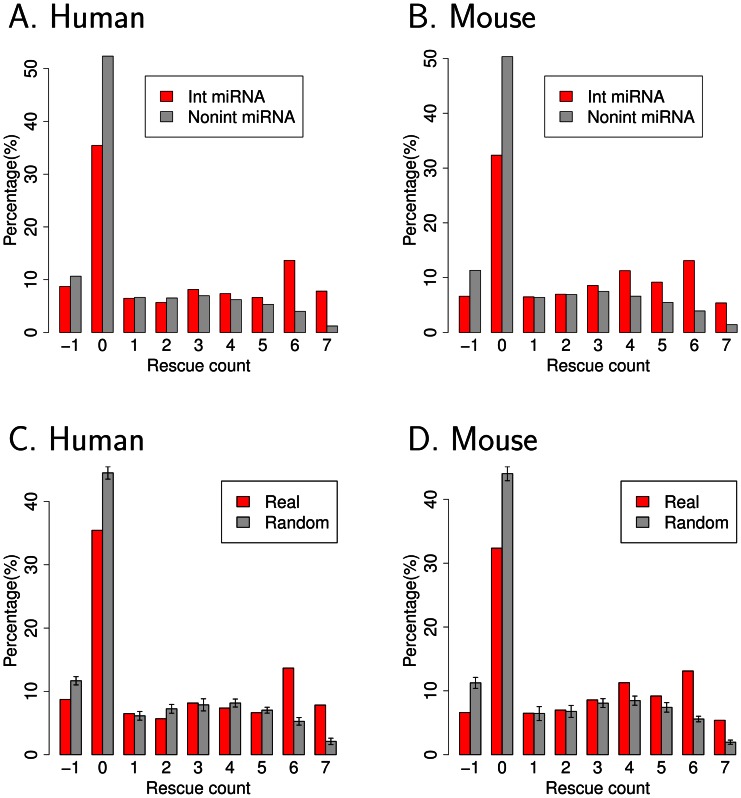
Figure 5. PUM rescues nucleotides in neighboring interacting miRNA recognition sites.
(A, B) For each PUM recognition site with a neighboring miRNA recognition site within 50 nts, the rescue count was computationally estimated as the number of nucleotides in the miRNA recognition site that PUM binding frees from hybridization with other nucleotides. The distributions of miRNA site rescue counts are shown in histograms for interacting miRNAs (red) and non-interacting miRNAs (gray) in human and mouse. (C, D) For all interacting miRNAs of PUM, the background model (Random) represents the histogram generated when RBP-miRNA paired site sequences were randomly shuffled while preserving mono and di-nucleotide frequency. Standard deviations were estimated from 10 randomizations.