Figure 1.
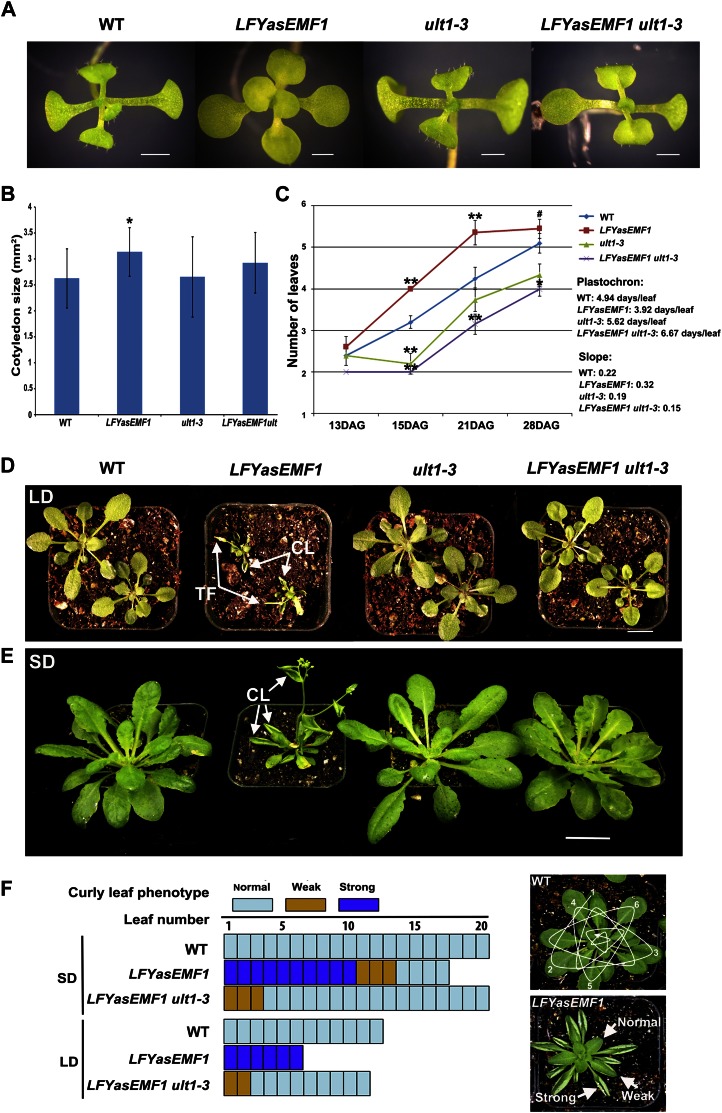
ult1-3 restores seedling and curly leaf phenotypes of LFYasEMF1. A, Three-week-old wild-type (WT), LFYasEMF1, ult1-3, and LFYasEMF1 ult1-3 plants grown on agar plates under SD conditions. The LFYasEMF1 cotyledons are flat and round, while those of the other three genotypes are slightly downward curled. B, Adaxial surface areas of the cotyledons of the four genotypes grown on agar plates under SD conditions. Significant difference from the wild type (Student’s t test) is marked with the asterisk (P < 0.05). C, Plastochron of the four plants grown on agar plates under SD conditions. The plastochron was calculated based on the slope of the number of days per leaf produced from 13 through 21 DAG. Significant differences from the wild type (Student’s t test) are marked with asterisks (* P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). The number sign indicates that the plants have bolted. D and E, Phenotypes of soil-grown LFYasEMF1 plants rescued by the ult1-3 mutation. Plants shown are 4 weeks old grown in LD (D) or 8 weeks old grown in SD in a greenhouse (E) after 2 weeks of growth on agar plates under SD conditions. CL, Curly leaf; TF, terminal flower. F, Curly leaf phenotype of LFYasEMF1 and LFYasEMF1 ult1-3 plants grown under LD and SD conditions. Blue areas, normal, not curly; brown areas, weak, mild curliness; purple areas, strong curliness. The top panel at right shows the strategy for counting leaf number from the bottom up, and the bottom panel at right shows variations in the extent of curliness. Bars = 1 mm (A), 1 cm (D), and 2 cm (E).