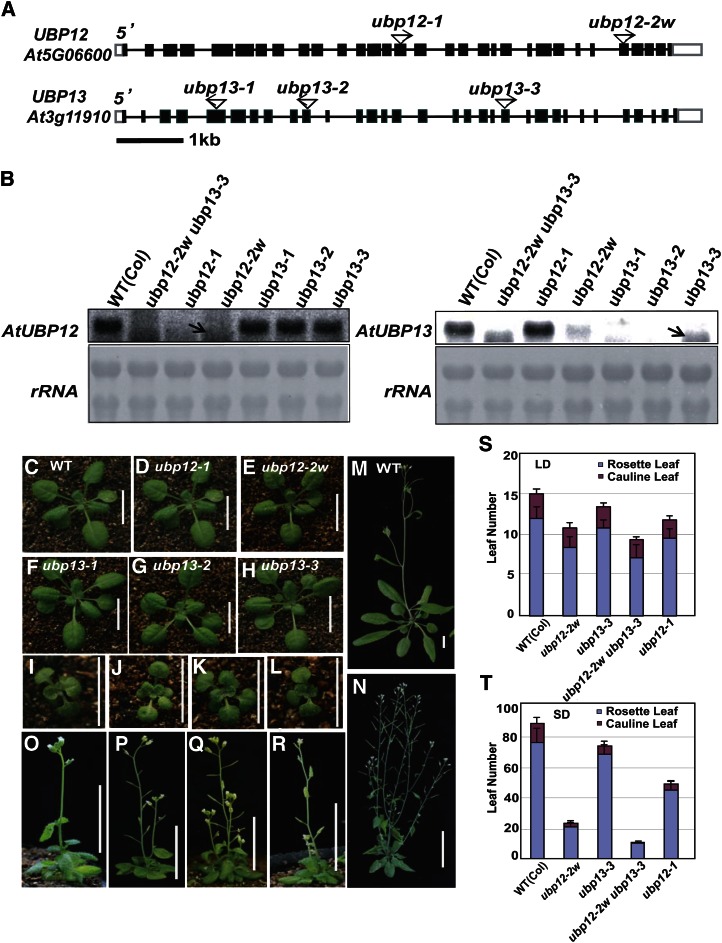
Figure 3.
Mutations of UBP12 and UBP13 affect plant development and flowering time. A, Schematic diagrams of the UBP12 and UBP13 gene structures, with the T-DNA insertion sites indicated. Black boxes indicate exons, white boxes indicate untranslated regions, and lines indicate introns. B, Northern blots showing the expression levels of UBP12 and UBP13 in the T-DNA insertion mutants (top). Ribosomal RNA stained with methylene blue was used as loading control (bottom). C to L, Phenotypes of 24-d-old seedlings of the wild type (C), ubp12-1 (D), ubp12-2w (E), ubp13-1 (F), ubp13-2 (G), ubp13-3 (H), ubp12-2w ubp13-1 (I), ubp12-2w ubp13-2 (J), ubp12-2w ubp13-3 (K), and ubp12-1 ubp13-3 (L). Bar = 1 cm. M to R, Phenotypes of the wild type (M), ubp12-2w (N), ubp12-2w ubp13-1 (O), ubp12-2w ubp13-2 (P), ubp12-2w ubp13-3 (Q), and ubp12-1 ubp13-3 (R) after bolting. Bar = 1 cm. S and T, Statistical analysis of leaf numbers of ubp12-2w, ubp13-3, ubp12-2w ubp13-3 double mutants, and ubp12-1 under LD (S) and SD (T) conditions compared with wild-type plants. Values are means ± sd of at least 20 plants. WT, Wild type.