Figure 2.
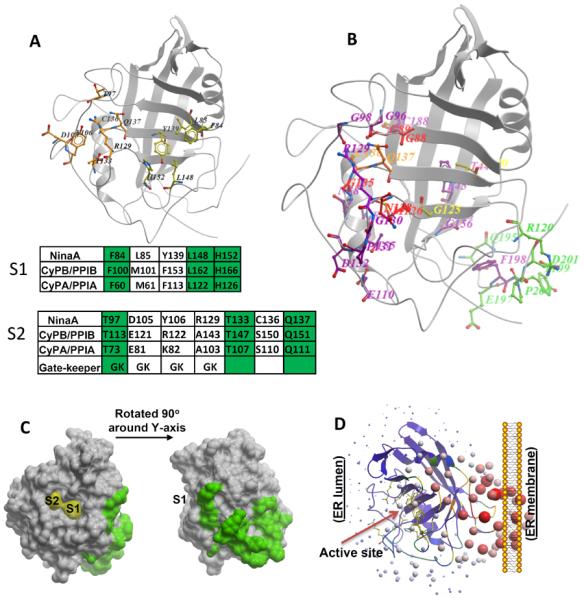
Assignment of physiological relevant residues of NinaA to new cylophilin domains. (A) Location of residues comprising S1 and S2 pockets as defined by Davis et al, 2010, in NinaA 3D-structure. Conservation of residues comprising the S1 and S2 pockets of NinaA, CyPB/PPIB and CyPA/PPIA are shown in the tables below the 3D-structure. The conservation of gatekeeper residues is also depicted. Identical residues are highlighted in green. (B) Mapping of residues caused by mutations in ninaA (Ondek et al., 1992; Table 1) to the 3D-model structure of NinaA. The mutations were grouped in five groups based on their location. Residues nearby the S1 pocket are in yellow, residues in the S2 pocket are in orange, residues in the S2 extended (S2e) region are in red, residues comprising Pm domain facing the membrane surface are in green, all other residues are in magenta. Note F198 points away from the surface. The S2e region comprises the residues, G88, G89, M126, N128 and G135. All residues, but N128, are buried in a shell next to the periphery of S2 binding pocket. (C) Surface representation of residues of Pm domain of NinaA and their relative location to S1 and S2 pockets. (D) Ribbon representation of the relative orientation of the PPIase active site of NinaA to its Pm domain. Active site residues are represented in the purple ribbons by sticks in yellow.
