Fig. 1.
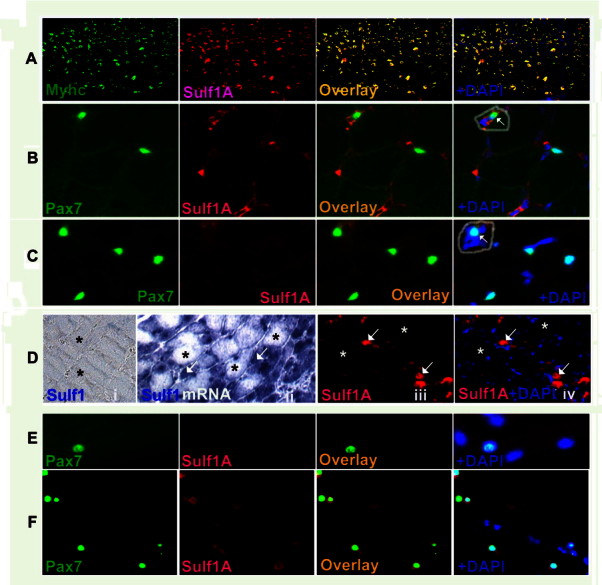
Sulf1A expressed in embryonic developing muscle becomes undetectable in adult muscle fibres and quiescent satellite cells but is re-activated in vitro and in vivo regenerating myogenic cells. For example, embryonic myotubes of a 7 day chick limb muscle express both skeletal muscle type myosin heavy chain and Sulf1A as is apparent from the individual and superimposed images (A). Unlike the embryonic muscle, neither adult chicken skeletal muscle fibres (B) or EDL muscle (C) from a 2-week old mouse or their Pax7-positive quiescent satellite cells show any Sulf1A staining by double immunofluorescence procedure. Unlike the skeletal muscle fibres and satellite cells, Sulf1A expression in the same sections is clearly detectable in endothelial cells of blood capillaries (B). Pax7-positive satellite-like cell present in a blood capillary is highlighted by a circle in (B). Pax7-positive satellite-like cell amongst interstitial cells is highlighted by a circle in (C). Myogenic Sulf1 expression, is re-activated in small sized myotubes of spontaneously regenerating myotubes indicated by white arrows while larger unaffected mature muscle fibres in EDL muscle of 4-week old mdx mouse show no Sulf1 expression at either mRNA (D.i, D.ii) or protein (D.iii, D.iv) levels (indicated by asterisks) using in situ hybridisation (D.i, D.ii) or immunofluorescence (D.iii, D.iv) procedures. Similarly, Sulf1A expression is undetectable in Pax7 positive quiescent satellite cells in isolated muscle fibres (E) at time 0 but detectable in most activated Pax7-positive satellite cells at 62 h (F) using double immunofluorescence procedure.
