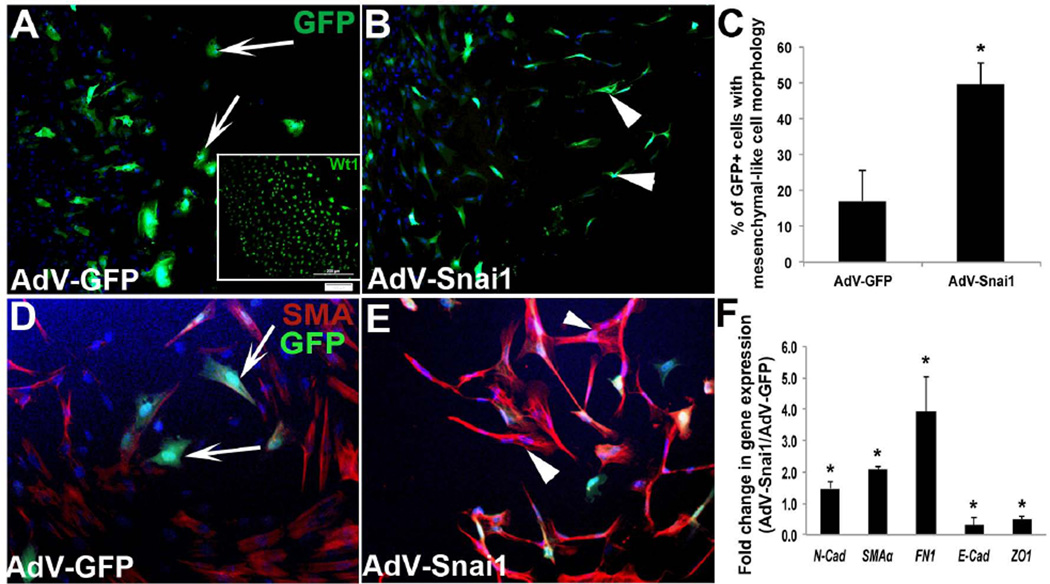
Figure 3. Snai1 overexpression enhances epicardial-to-mesenchymal transformation in avian epicardial explants.
Epicardial cell outgrowths from HH St. 24 whole heart explants were infected with AdV-GFP (A, D) or AdV-Snai1 (B, E) for 48 hours and differences in cell morphology (A, B), protein (D, E) and gene (F) expression were analyzed. (A) GFP-positive spherical epicardial cells were observed in cultures infected with AdV-GFP (arrows, A), while fibroblast-like mesenchyme cells (arrowheads) were apparent in AdV-Snai1 infected epicardial cells (B). Inset in (A) shows Wt1 immunohistochemistry to indicate the epicardial phenotype of these cells prior to treatment. (C) Quantitation of the percentage of GFP+ cells that display fibroblast-like mesenchyme cell morphology in AdV-GFP and AdV-Snai1 infected cells. (D) Representative immunohistochemistry to detect SMA expression in AdV-GFP (D) and AdV-Snai1 (E) infected epicardial cells. Arrows in D indicate rounded cells types, and arrowheads in E highlight mesenchymal shaped cell types. (F) qPCR to examine changes in expression levels of N-cad (N-cadherin), SMAα (Smooth muscle α-actin), FN1 (Fibronectin-1), E-cad (E-cadherin) and ZO-1 in AdV-Snai1 infected cells compared to AdV-GFP (n=3). * =p<0.05.