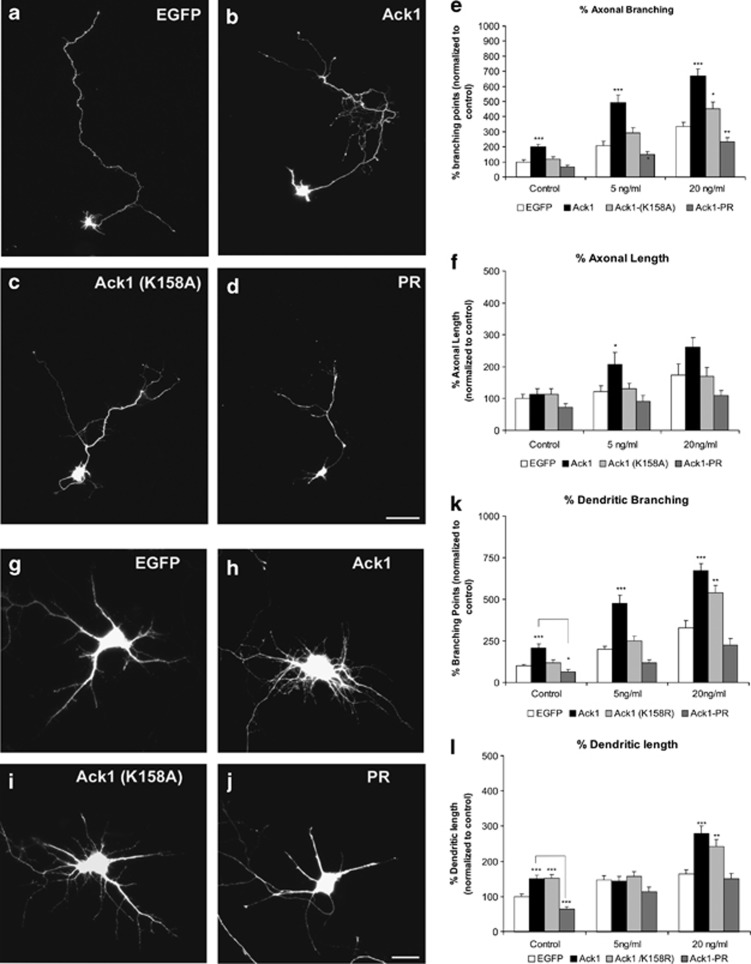
Figure 7.
Ack1 enhances BDNF-dependent neuritic outgrowth and branching in hippocampal neurons. Primary hippocampal neurons were transfected with pEGFP (a and g) or co-transfected with pEGFP and Ack1 (b and h), Ack1 (K158A) (c and i) or the proline-rich construct (d and j), at day 4 in vitro and fixed 3 days later. Neurons were treated with a range of dosages of BDNF (control experiment, 5 or 20 ng/ml of BDNF). (a–d) Untreated cells and (g–j) transfected neurons treated with 5 ng/ml of BDNF for 2 days are shown. The number of branching points of axons and dendrites of GFP-immunopositive neurons was markedly increased upon Ack1 overexpression, as also shown by quantitative analyses (e and k). The length of axons (f) and dendrites (l) was also measured in GFP-immunopositive neurons. The data are represented as mean±S.E.M. of five separate experiments. Data were normalized to control values (pEGFP transfection). Each treatment group at 5 and 20 ng/ml was compared with its corresponding control using the T-test (*P<0.01; **P<0.05; ***P<0.001). Scale bars: (a–d) 25 μm; (g–j) 15 μm