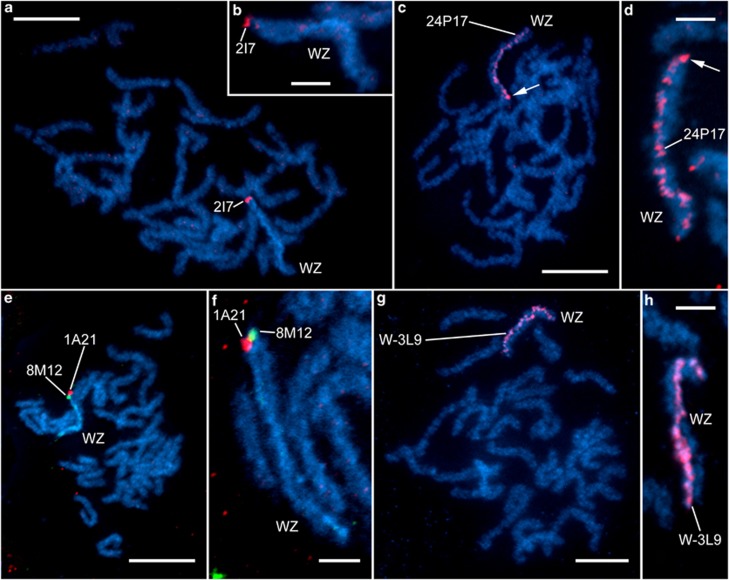
Figure 5.
BAC-FISH mapping on both sex chromosomes (W and Z) in female B. betularia. Hybridization patterns of four laminin A-containing clones and one W-linked AFLP marker-derived clone on W and Z chromosomes. (a, c, e, g) Pachytene oocyte complements. (b, d, f, h) Details of WZ bivalents. Chromosomes were counterstained with DAPI (light blue); BAC probes were labeled with Cy3-dUTP (red) or Alexa Fluor 488-dUTP (green). The sex chromosome bivalent (WZ) is discernible from a DAPI-positive heterochromatic thread of the W chromosome and also by hybridization signals of the BAC probes. (a, b) laminin A BAC probe 2I7 (red) shows hybridization signals at the end of both the W and Z chromosomes. (c, d) laminin A BAC probe 24P17 (red) shows scattered hybridization signals along the whole W-chromosome thread; a stronger signal at one end of the W chromosome (arrow) possibly indicates a physical position of the BAC clone. (e, f) laminin A BAC probes 1A21 (red) and 8M12 (green) indicate physical positions of laminin A at the ends of the Z and W chromosomes, respectively. (g, h) AFLP-derived BAC probe W-39L (red) paints the entire W-chromosome thread. Scale bars=10 μm (a, c, e, g) or 3 μm (b, d, f, h).