Figure 4. ROS induces cell death and mitochondrial apoptotic signaling in FHs74 Int cells.
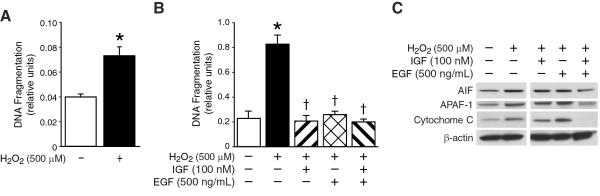
(A) FHs74 Int cells were treated with H2O2 (500 μM) as before. Apoptosis was measured by DNA fragmentation ELISA. Data represent triplicate determinations (mean ±SEM; *p<0.05 vs. control). H2O2 treatment resulted in significant cellular apoptosis. (B) FHs74 Int cells were serum starved, pretreated with IGF-1, EGF or in combination and then treated with H2O2 as before. Apoptosis was measured by DNA fragmentation ELISA. Data represent triplicate determinations (mean ±SEM; *p<0.05 vs. control, †p<0.05 vs. H2O2-treated FHs74 Int cells). IGF-1- and EGF-pretreated FHs74 Int cells showed increased survival during oxidative stress. (C) FHs74 Int cells were serum starved, pretreated with IGF-1, EGF or in combination and then treated with H2O2 as before. H2O2 treatment resulted in significant increases in AIF, APAF-1 and cytochrome C expression by Western blotting. There was significant attenuation of this effect when FHs74 Int cells were pretreated with both IGF-1 and EGF, suggesting synergistic effect on modulating mitochondrial apoptotic pathway activation. Equal β-actin levels indicate even loading.
