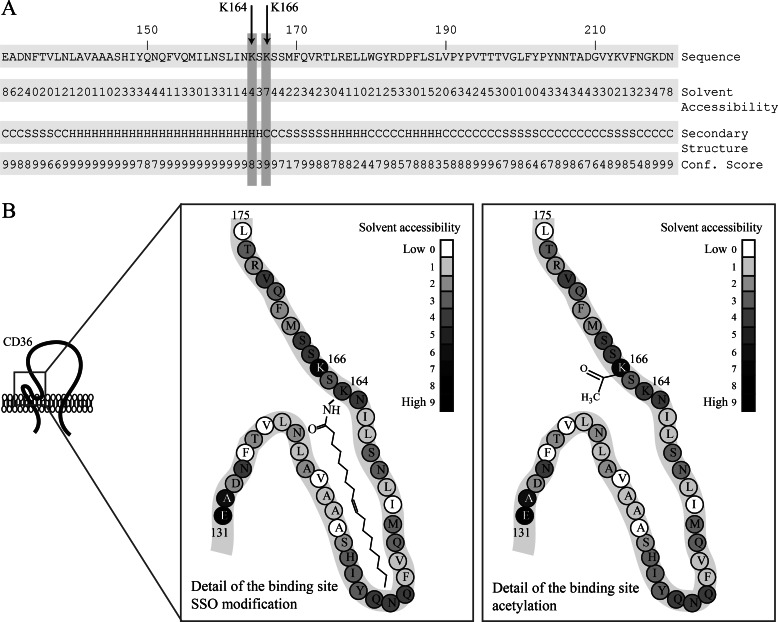
FIGURE 4.
Structural prediction of the SSO-binding site in CD36. A, prediction of the secondary structure of the CD36 sequence (UniProt P16671) containing the SSO-binding site using the I-TASSER platform. Predicted secondary structures: C, coil; S, sheet; H, helix; confidence scores range from 0 (low) to 10 (high). Predicted solvent accessibility of amino acid residues: 0 (buried) 9 (exposed). B, schematic model of the CD36-binding site for long-chain FA. Lysine 166 is predicted to be solvent-exposed, although Lys-164 is predicted to be less solvent-accessible. Gray scale is based on I-TASSER predictions. Lys-164 can be modified by SSO to yield N-oleoyl amide, which occupies the putative hydrophobic pocket (left panel). Lys-166 can be acetylated, and this modification might modify accessibility of the pocket (right panel).