FIGURE 1.
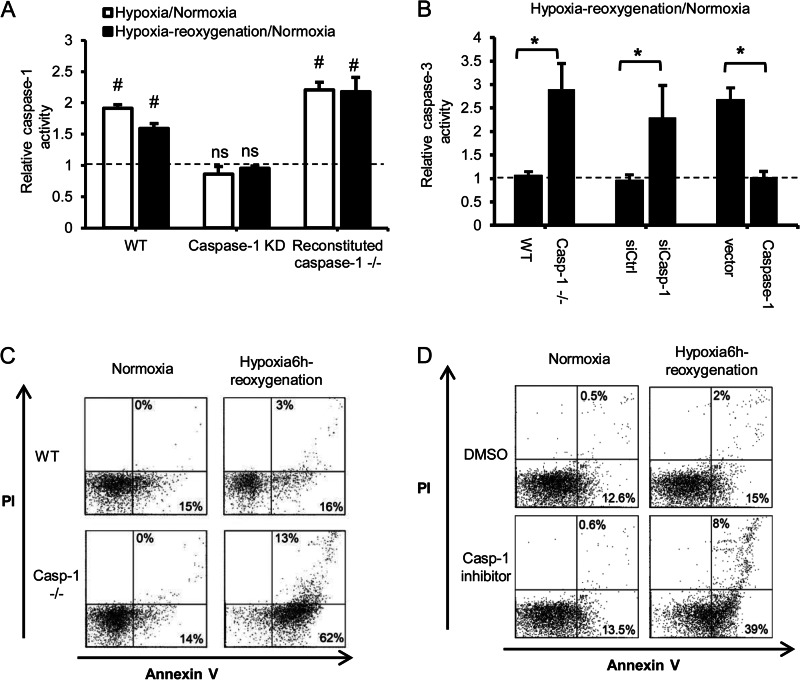
Caspase 1 is protective in hepatocytes after hypoxia/reoxygenation. A, relative caspase 1 activity in WT hepatocytes, WT hepatocytes treated with caspase 1 siRNA, and caspase 1−/− cells transfected with mouse caspase 1 plasmid after normoxia, 6 h of hypoxia, or 6 h of hypoxia/1 h of reoxygenation. Data are shown as fold changes of normoxic levels. Data are mean ± S.D, n = 3. #, p < 0.05, normoxia versus hypoxia-reoxygenation; ns, not significant. B, relative caspase 3 activity in WT and caspase 1−/− hepatocytes, WT hepatocytes treated with caspase 1 siRNA, and caspase 1−/− cells expressing mouse caspase 1 after 6 h of hypoxia/1 h of reoxygenation. Data are shown as fold changes of normoxic levels. Data are mean ± S.D., n = 3. *, p < 0.05. C, representative annexin V/PI flow cytometry dot plots for hepatocytes cultured under normoxia or after 6 h of hypoxia/1 h of reoxygenation. D, representative annexin V/PI analysis of WT hepatocytes pretreated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or caspase 1 inhibitor (15 μm) and then 6 h of hypoxia/1 h of reoxygenation. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments.