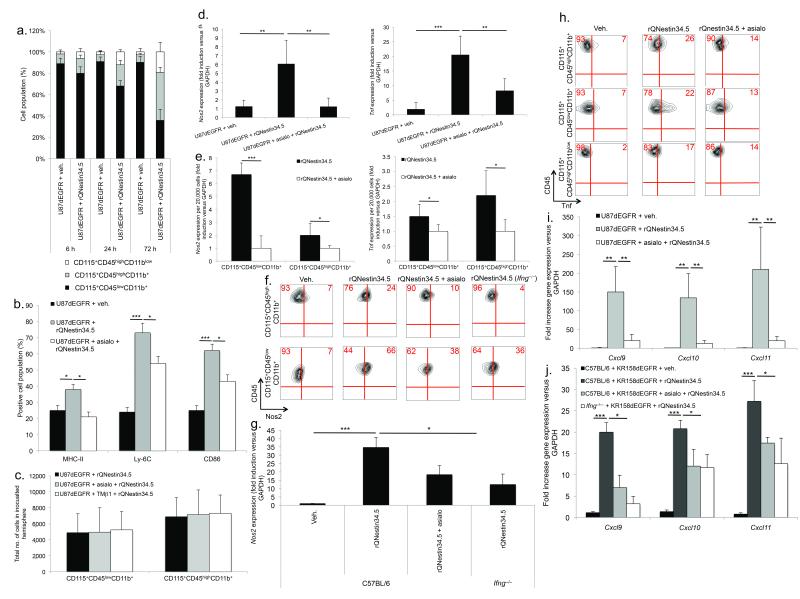
Figure 3. NK cells mediate macrophage and microglia activation following oHSV therapy.
(a) FACS of time-dependent changes in CD115+CD45highCD11b+, CD115+CD45highCD11blow and CD115+CD45lowCD11b+ cells in glioblastomas following rQNestin34.5 (n = 4–6 mice/group). (b) FACS of CD115+CD45highCD11b+ cells expressing macrophage activation markers (MHC-II, Ly-6C, or CD86), 72 hours after vehicle or rQNestin34.5 infection as a function of NK cell presence (n = 4/group). (c) FACS of CD115+CD45lowCD11b+ or CD115+CD45highCD11b+ cells 72 hours after rQNestin34.5 inoculation as a function of NK cell presence. (d) Nos2 and Tnf expression in tumor bearing hemispheres, 72 hours following vehicle or rQNestin34.5 inoculation in the presence or absence of NK cells (n = 4–5/group). (e) Nos2 and Tnf expression, as a function of NK cell depletion, in FACS sorted CD115+CD45lowCD11b+ or CD115+CD45highCD11b+ cells 72 hours after rQNestin34.5 inoculation of U87dEGFR. (f, g) Intracellular protein staining with FACS quantification (f) and Nos2 mRNA expression (g) in intracranial KR158dEGFR tumors, 72 hours after rQNestin34.5 inoculation as a function of NK cells and Ifng production. (h) FACS of intracellular Tnf 72 hours after rQNestin34.5 treatment of U87dEGFR as a function of NK cell presence. (i, j) Cxcl9, Cxcl10, and Cxcl11 expression 72 hours after rQNestin34.5 treatment of both xenograft (i) and syngeneic (j) tumors as a function of NK cell presence (n = 3–5/group). The dependence of Ifng in gene expression within the KR158dEGFR was also assessed. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001. Error bars represent +/− standard deviation.