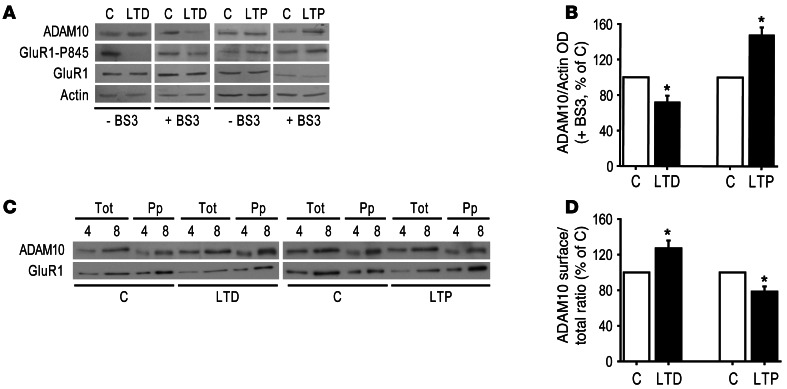
Figure 6. LTD promotes ADAM10 insertion into the membranes, whereas LTP reduces ADAM10 membrane levels.
(A) Immunoblot of ADAM10, GluR1-P845, GluR1, and actin from control and cLTD/cLTP-treated hippocampal cultures either exposed or not exposed to the crosslinker BS3. cLTD leads to a significant decrease in ADAM10 intracellular pool, which reflects an augment in ADAM10 surface expression. cLTP significantly increases ADAM10 intracellular pool because cLTP results in a decrease in ADAM10 membrane localization. As expected, cLTD induction reduces and cLTP increases the Ser-845 phosphorylation of GluR1. (B) Quantification of the ADAM10/Actin OD ratio of BS3-treated neurons of experiments in A (*P < 0.05 cLTD versus C, n = 7, cLTP versus C, n = 3). (C) After either cLTD or cLTP induction, hippocampal cultures were biotinylated and the extracts were precipitated with neutravidin. To avoid saturation of band signal in order to carry out precise quantitative analyses, samples of extracts (Tot) and neutravidin-precipitated samples (Pp) were loaded such that each lane represents a percentage of the total material per plate. Representative immunoblot of ADAM10 and GluR1 from control and treated cultures. (D) ADAM10 OD in Pp samples (surface) was measured and normalized to ADAM10 OD in tot samples (total) to calculate the surface/total ratio. Quantification of the surface/total ratio of experiments in C (*P < 0.05 cLTD versus C, n = 5, cLTP versus C, n = 6).