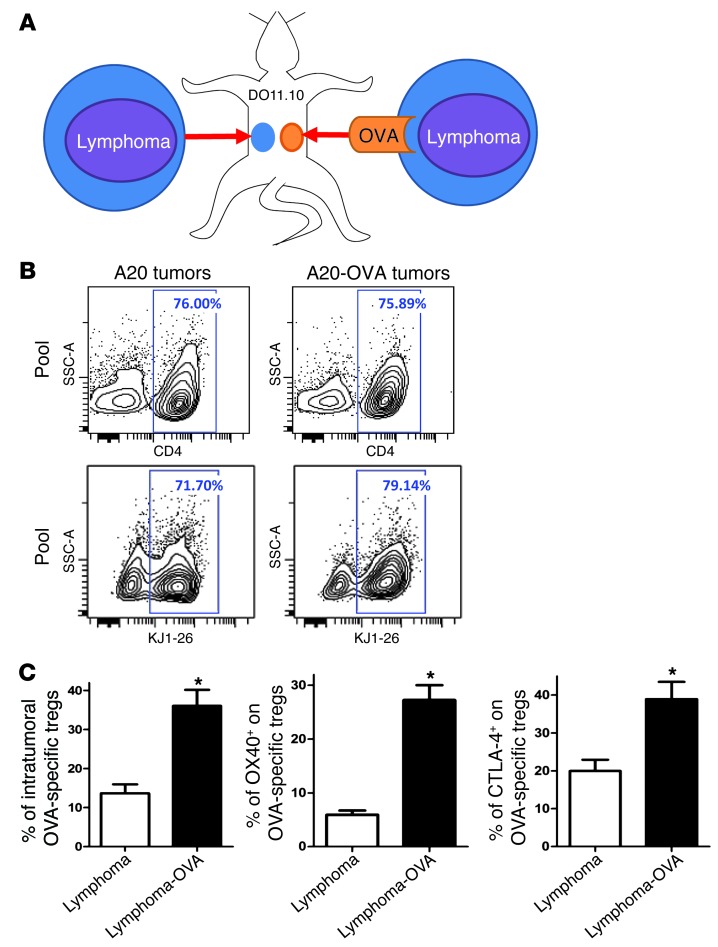
Figure 2. OX40 and CTLA-4 are highly expressed at the tumor site, especially by tumor-specific Tregs.
(A) DO11.10 mice were transplanted s.c. with A20 lymphoma tumor cells at one site and with A20-OVA at another (5 × 106 cells per site). About 70% of CD4+ T cells from DO11.10 mice are directed against the OVA peptide. They can be identified by the KJ1-26 clonotypic mAb, which specifically binds their OVA-specific TCR. (B) 10 days after challenge, tumors were collected and tumor-infiltrating OVA-specific T cells (KJ1-26+) were analyzed by FACS (pool of tumors from 5 mice). (C) The proportion of FOXP3+ cells within the OVA-specific CD4+ T cells (gated on KJ1-26+) and the proportion of expression of OX40 and CTLA-4 within the OVA-specific Tregs (gated on CD4+KJ1-26+FOXP3+) (mean ± SEM, n = 5, *P < 0.05).