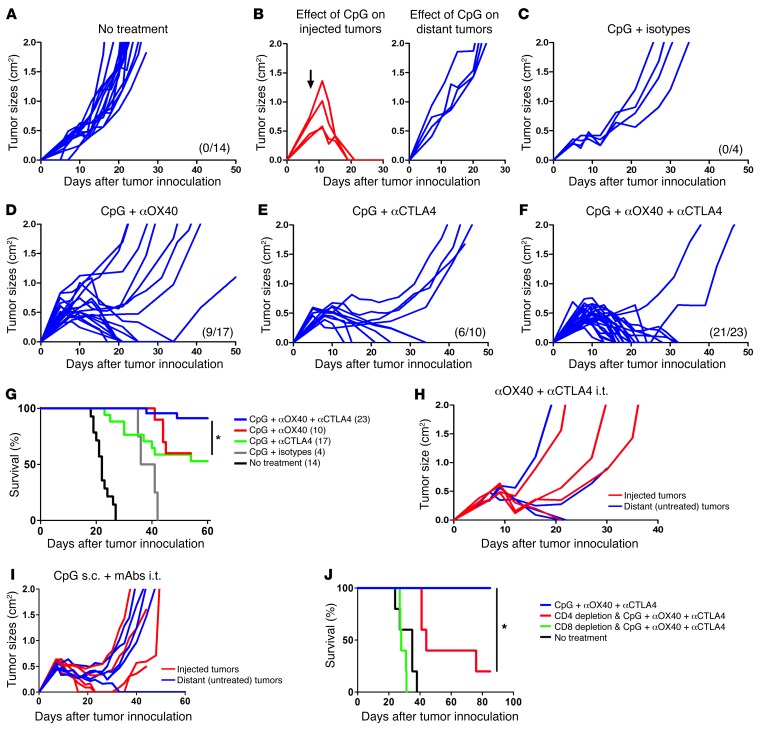
Figure 4. Combination therapy of i.t. CpG and low-dose immunomodulatory antibodies is specifically required to trigger an efficient antitumor immune response.
Mice were treated as in Figure 3A, and. i.t. injections of therapy were done in right (local) tumors (red), and systemic antitumor effect was assessed by measuring growth of left (distant) tumors (blue). CpG was injected at 100 μg daily for 5 consecutive days. Low doses of mAbs (4 μg αOX40 or rat isotype or/and 1 μg αCTLA4 or hamster isotype) were injected on day 1 and 5 of CpG therapy into the same tumor. (A) Growth of distant tumors without therapy. (B–F) Systemic antitumor effect of CpG injections (B) alone on injected and distant tumors; (C) in combination with rat and hamster isotypes of αOX40 and αCTLA4 mAbs, respectively; (D) in combination with αOX40; (E) in combination with αCTLA4; and (F) in combination with αOX40 and αCTLA4. Previous curves pooled from at least 2 different experiments per group. (A–F) The number of surviving mice at day 60 is shown in parenthesis. (G) Survival of mice bearing 2 s.c. tumors (right and left flanks) that received CpG plus rat/hamster isotypes, CpG plus αOX40, CpG plus αCTLA4, or CpG plus αOX40/CTLA4 in right tumors. Survival with CpG plus αOX40/CTLA4 was significantly higher than with CpG plus αOX40 (P = 0.004) or CpG plus αCTLA4 (P = 0.03). Data are pooled from at least 2 different experiments per group; the number of mice per group is shown into parenthesis (*P < 0.05). Systemic antitumor effect of (H) αOX40 plus αCTLA4 local low-dose therapy without CpG (n = 4) and (I) s.c. CpG and i.t. αOX40 plus αCTLA4. (J) Survival of tumor-bearing mice treated with i.t. CpG and low-dose αOX40 plus αCTLA4 in the context of CD4 or CD8 T cell depletion (*P < 0.05).