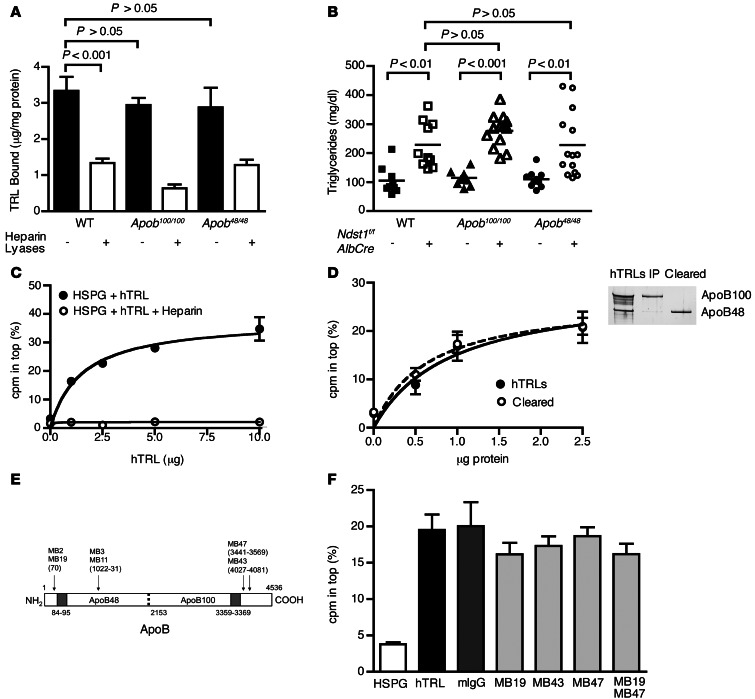
Figure 3. TRL binding to heparan sulfate is independent of ApoB.
(A) Binding of [3H]TRLs from Apob100/100 and Apob48/48 mice to Hep3B cells was measured before (filled bars) or after (open bars) treatment with heparin lyases (n = 4). Binding of WT [3H]TRLs done at the same time is repeated here from Figure 1B for comparison. (B) Fasting plasma triglycerides from Apob100/100Ndst1f/fAlbCre– (n = 12, filled triangles), Apob100/100Ndst1f/fAlbCre+ (n = 13, open triangles), Apob48/48Ndst1f/fAlbCre– (n = 8, filled circles) and Apob48/48Ndst1f/fAlbCre+ (n = 13, open circles) mice were measured. Plasma triglycerides from Ndst1f/fAlbCre– animals (squares) are included from Figure 2B for comparison. (C) Binding of purified [35S]HSPG ectodomains to human TRLs (hTRL) was measured by ultracentrifugation (see Methods). Binding of [35S]HSPGs to human TRLs (filled circles) occurred in a saturable manner and was inhibited by heparin (open circles). (D) Binding of [35S]HSPGs to ApoB48 only (open circles) or mixed human TRLs (filled circles) was measured. SDS-PAGE and silver staining for ApoB of purified human TRLs is also shown. (E) Diagram of epitope map for ApoB mAbs. Specific residues recognized by Abs are shown in parentheses, and heparin binding sites are shaded gray. Image is not drawn to scale. (F) [35S]HSPG binding to human TRLs was measured by ultracentrifugation in the absence (black bar) or presence of mouse IgG (dark gray bar) or mAbs specific for domains spanning ApoB (MB19, MB43, and/or MB47; light gray bars). A control experiment done without human TRLs (white bar) is shown for comparison.