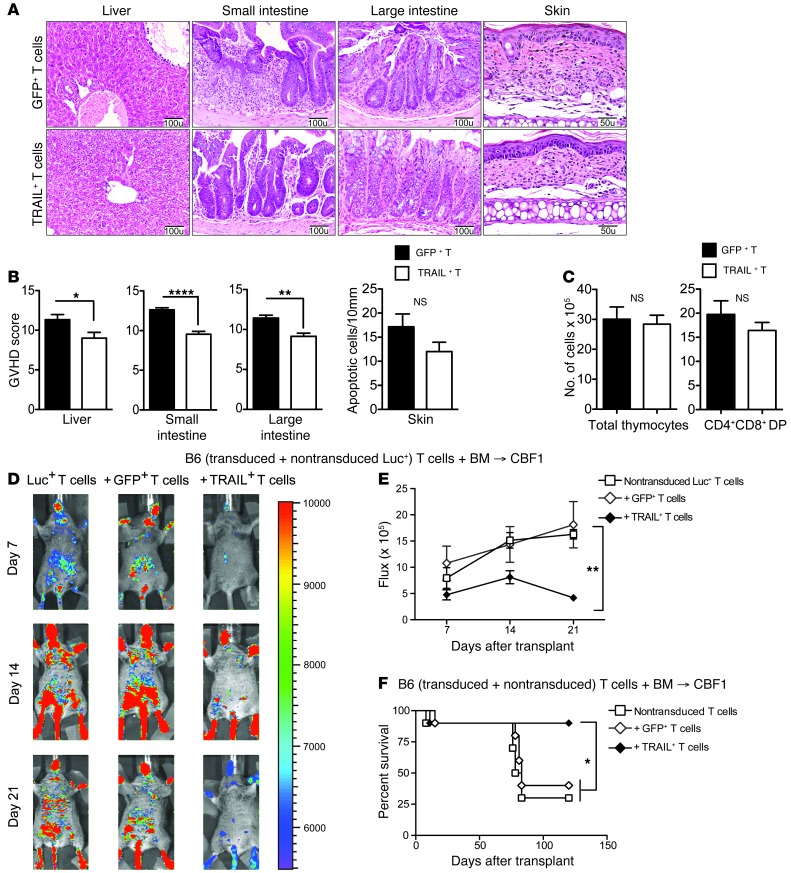
Figure 3. TRAIL+ T cells suppress GVHD.
(A and B) Livers and small and large intestines from B6→CBF1 mice treated with GFP+ or TRAIL+ T cells were harvested on day 14 after BMT and skin was harvested on day 21 and scored for GVHD pathology. Representative micrographs are shown (original magnification, ×200 for liver, small and large intestines; and ×400 for skin). GVHD scores pooled from 2 independent experiments are shown (n = 8–10 per group). (C) Thymi from B6→CBF1 mice treated with GFP+ or TRAIL+ T cells were harvested on day 21 after BMT. Total cellularity was obtained from counts of live thymocyte suspension and numbers of DP T cells were derived from flow cytometric determination of CD4+CD8+ T cell proportions. Data pooled from 2 independent experiments are shown (n = 8–10 per group). (D and E) Lethally irradiated CBF1 recipients were reconstituted with 5 × 106 cells per recipient of B6 TCD BM. Designated groups were treated with 0.5 × 106 cells per recipient of GFP+ or TRAIL+ T cells mixed with nontransduced Luc+ T cells. Bioluminescence imaging of the transplanted mice was performed weekly (D) and flux was measured (E). Animals representative of 1 experiment (n = 7 per group) and flux pooled from 3 independent experiments are shown. (F) Lethally irradiated CBF1 recipients were reconstituted with 5 × 106 cells per recipient of B6 TCD BM. Designated groups were treated with 0.5 × 106 cells per recipient of GFP+ or TRAIL+ T cells mixed with nontransduced T cells (n = 10 per group). Survival was monitored daily. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ****P < 0.0001. NS, not significant.