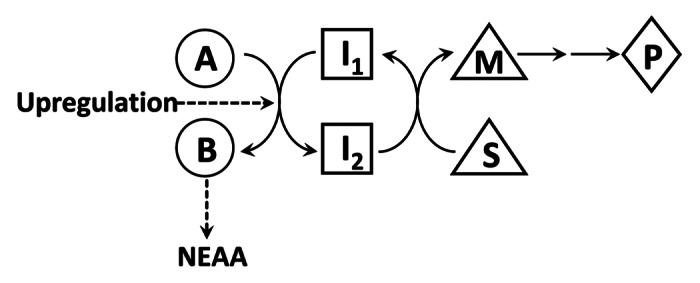
Figure 1. Proposed Parametabolic Regulation by NEAA Metabolism This cartoon is a representation of a generic parametabolic scheme. The conversion of A to B yields a non-essential amino acid and this step may be upregulated by cancer reprogramming. I1 and I2 are in a metabolic interlock with the conversion of S to M, which is then used for epigenetic modification of DNA or chromatin. For example, if A is serine and B is glycine, the reaction is coupled to the conversion of tetrahydrofolate (THF) to 5,10-methylene THF, which as 5-methyl THF, transfers methyl groups to homocysteine forming methionine. In the presence of ATP, S-adenosylmethionine is formed for DNA methylation. In another example, if pyrroline-5-carboxylate, A, is converted to proline, B, NADH, I1, is oxidized to NAD+, I2, which can accept acetyl groups hydrolyzed from histone lysines by sirtuins to form acetyl-ADP-ribose.
