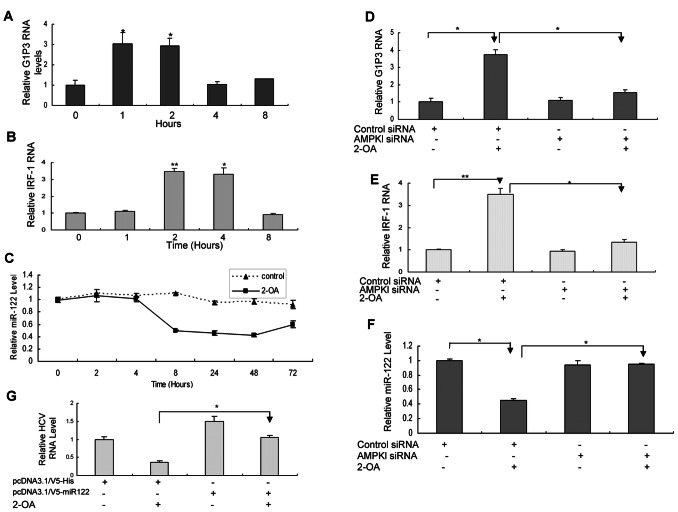
Figure 5. 2-OA induces ISGs and inhibits the expression of miR-122 through activated AMPK.
(A)/(B) 2-OA induces G1P3 (A) and IRF-1 (B) in HCV-infected Huh7.5. Virus-infected cells were incubated with 100 µM 2-OA for different time periods. G1P3 (A) or IRF-1 (B) RNA was detected with real-time PCR. The expression of G1P3 or IRF-1 was normalized with GAPDH. The data represented the means of 3 different experiments. (C) 2-OA suppresses miR-122 expression in HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells. Virus-infected hepatocytes were treated with 100 µM 2-OA for different time periods. MiR-122 was detected with real-time PCR. The expression of miR-122 was normalized with GAPDH. (D)/(E) Knockdown of AMPK by AMPK siRNA abrogates the induction of G1P3 and IRF-1 by 2-OA. Virus-infected Huh7.5 cells pretransfected by AMPK siRNA or control siRNA were incubated with 100 µM 2-OA for 2 hours. G1P3 (D) or IRF-1 (E) RNA was detected with real-time PCR. The expression of G1P3 or IRF-1 was normalized with GAPDH. (F) Knockdown of AMPK by AMPK siRNA reverses the inhibition of miR-122 by 2-OA. HCV-infected Huh7.5 cells pretransfected by AMPK siRNA or control siRNA were treated with 100 µM 2-OA for 48 hours. MiR-122 was detected with real-time PCR. The expression of miR-122 was normalized with GAPDH. (G) MiR-122 overexpression reversed the antiviral effect of 2-OA. MiR-122 was overexpressed in HCV-infected cells and the cells were treated by 100 µM 2-OA for 48 hours. Total cellular RNA was isolated from the cells. HCV RNA was detected by real-time PCR analysis and normalized with GAPDH.