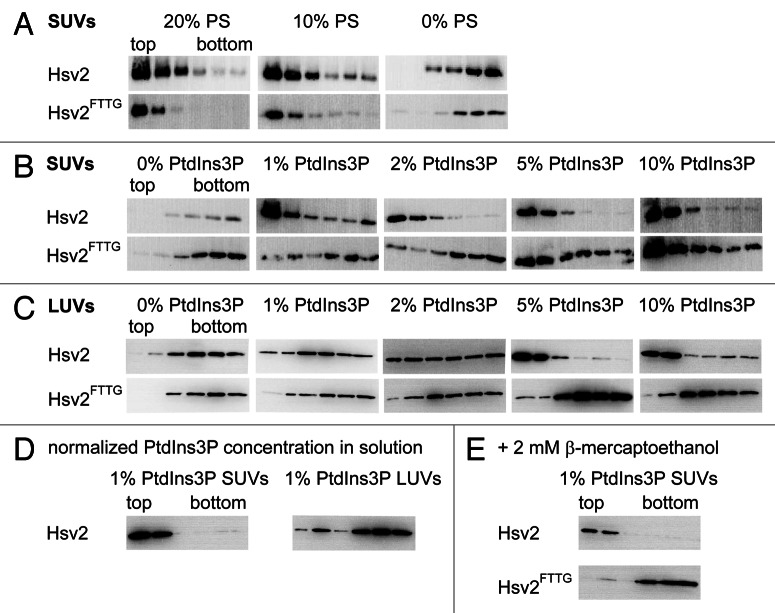
Figure 2. Optimization of liposome lipid composition. (A) Hsv2 and Hsv2FTTG bound nonspecifically to SUVs containing either 10% or 20% PS. Both proteins did not interact with neutral liposomes consisting of 0% PS, 75% PC, 23% PE, 2% Texas-Red-PE. (B) PtdIns3P was added stepwise to neutral SUVs consisting of PC, PE and Texas-Red-PE (x% PtdIns3P, (75-x)% PC, 2% Texas-Red-PE, 23% PE). At 1% and 2% PtdIns3P only Hsv2 bound to the liposomes, whereas at a PtdIns3P concentration of 5% and above both wild-type and mutant Hsv2 bound nonspecifically. (C) PtdIns3P concentration was gradually increased in LUVs (x% PtdIns3P, (75-x)% PC, 2% Texas-Red-PE, 23% PE). Wild-type Hsv2 bound completely to 5% and 10% PtdIns3P-containing LUVs. Hsv2FTTG did not bind to LUVs. (D) 1% PtdIns3P-containing SUVs and LUVs with the same PtdIns3P accessible surface concentration in solution were used for flotation assays. (E) Binding of wild type and Hsv2FTTG to 1% PtdIns3P-containing SUVs was analyzed for samples treated with 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.