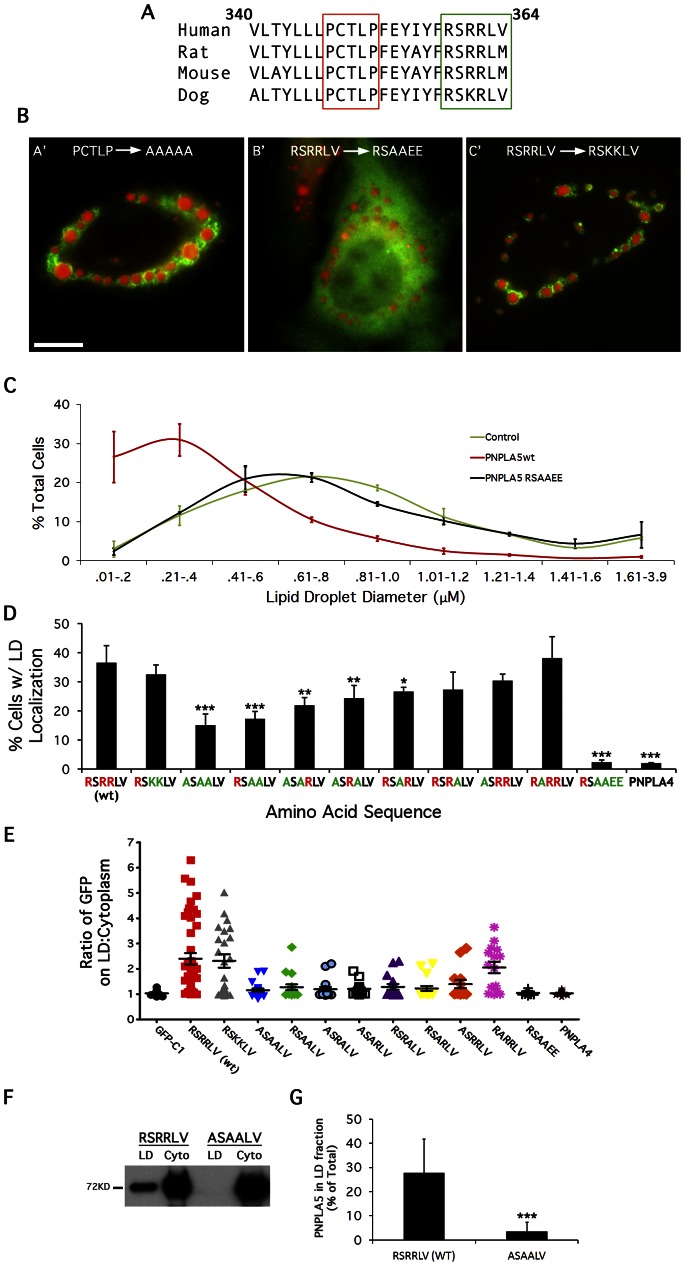
Figure 4. Alterations in the basic charge LTM of PNPLA5 abolish LD localization.
(A) Comparison of amino acid sequences 340–364 of PNPLA5 between several species. Boxed in red are the conserved proline-rich and arginine-rich domains. (B) HeLa cells were treated overnight with OA, transfected with the indicated constructs for 24 h, fixed and stained with LipidTOX Red. Cells were then analyzed by fluorescence microscopy and scored for LD localization. GFP-PNPLA5(A347AAAA352) and GFP-PNPLA5(K360KLV363) localized to LDs, whereas GFP-PNPLA5(A360AEE363) was cytoplasmic (quantified in D). Bar, 5 μm. (C) Quantitation of LD diameters showed that overexpession of wildtype GFP-PNPLA5 reduced LD size, whereas LDs in cells over-expressing GFP-PNPLA5(A360AEE363) were similar to those in control cells. (D) Different combinations of arginines in the LTM were mutated within full length GFP-tagged PNPLA5 and LD localization was observed. No single arginine was critical for LD association but removal of each one incrementally reduced LD binding. Data are plotted as means ± SEM; ≥3 experiments/condition; ≥300 cells counted/experiment; ***indicates p<0.0001, **indicates p<0.001, *indicates p<0.05 compared to wildtype (RSRRLV). (E) Quantitation of fluorescence intensity on LD surface:cytoplasm ratio from line plots (n≥15 LDs and cells/condition). (F) HeLa cells were treated as in ‘B’ except transfections were followed by cell fractionation. Wildtype PNPLA5 (RSRRLV), but not the mutant lacking all three arginines in the basic patch (ASAALV), was enriched on LDs as shown by western blotting of isolated LD fractions in comparison to pooled cytoplasmic fractions (cyto); quantitation in (G). Data are plotted as means± SEM, n = 3.