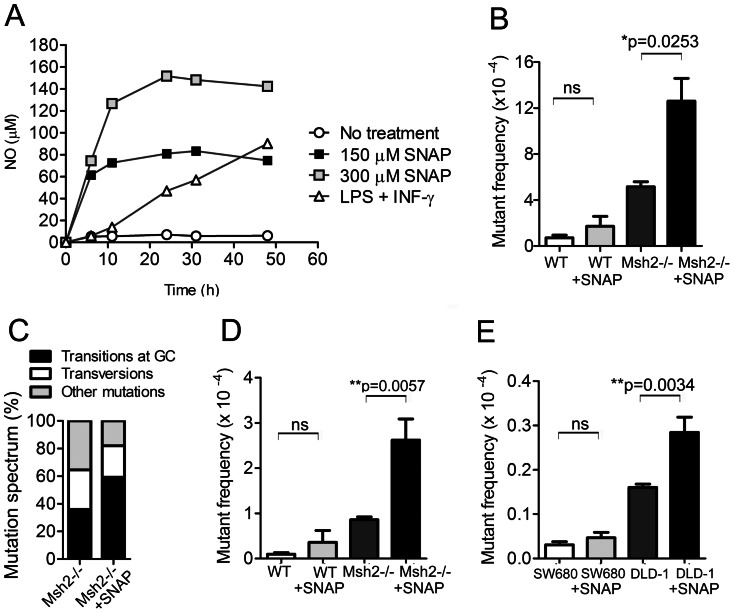
Figure 1. Nitric oxide induces DNA mutations that are repaired by the MMR pathway.
(A) Measurements of the amounts of nitric oxide in culture medium generated by various concentrations of SNAP or by macrophages that were stimulated by LPS and IFN-γ. (B) The mutant frequency at the lacI gene in Msh2+/− (WT, n = 3) and Msh2−/− (n = 3) SNAP-treated or non-treated macrophages was measured by the Big Blue mutagenesis screen. Bone marrow-derived macrophages were cultured in presence of 150 µM SNAP for 20 hrs. Genomic DNA was isolated and the mutant frequency at lacI gene was calculated. (C) Mutation spectrum in SNAP-treated macrophages as determined by sequencing analysis. The C:G → T:A transitions are shown. The tranversion mutations include C:G → A:T, C:G → G:C, T:A → G:C and T:A → A:T substitutions. The insertions and deletions are presents as other mutations. (D) The mutant frequency at the hprt gene in Msh2+/− (WT, n = 8) and Msh2−/− (n = 8) SNAP-treated or non-treated Pre-B cells. (E) The mutant frequency at the hprt gene in SW680 (n = 8) and DLD-1 (n = 8) SNAP-treated or non-treated human colorectal cancer cell lines.