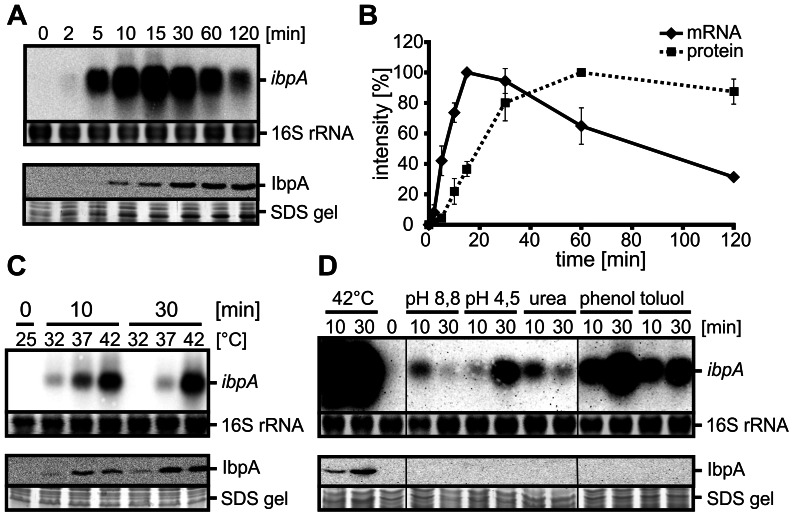
Figure 2. Transcriptional and translational regulation of the P. putida ibpA.
A. Heat induction of ibpA transcript (444 nt) and IbpA protein (16.1 kDa). P. putida cells were grown to OD600 0.5 at 25°C and heat-shocked at 42°C. Samples were taken at the indicated time points after the temperature upshift and probed by Northern and Western blot analyses. Upper panel: Northern blot and ethidiumbromide-stained 16S rRNA as loading control; lower panel: Western blot and corresponding section of the SDS gel. B. Quantification of ibpA transcript and IbpA protein amounts. Signal intensities were quantified with the Alpha Ease software, normalized to the strongest signals and plotted (ibpA mRNA: solid line, IbpA protein: dashed line). C. ibpA transcript and IbpA protein amounts at different heat stress scenarios. P. putida cultures were grown to OD600 0.5 at 25°C and split to 32, 37 and 42°C. Samples were harvested 0, 10 and 30 min after temperature shift and analyzed via Northern and Western analyses as in 2A. D. Influence of various stresses on ibpA expression and IbpA protein synthesis. P. putida cells were grown to OD600 0.5 at 25°C and exposed to following stress conditions: heat (42°C), osmotic stress (0.8 M urea), acidic stress (∼pH 4.5 with HCl), alkaline stress (∼pH 8.8 with NaOH), phenol (15 mM) and toluol (12 mM). Samples for Northern and Western analyses were taken 10 and 30 minutes after stress induction and analyzed as in 2A.