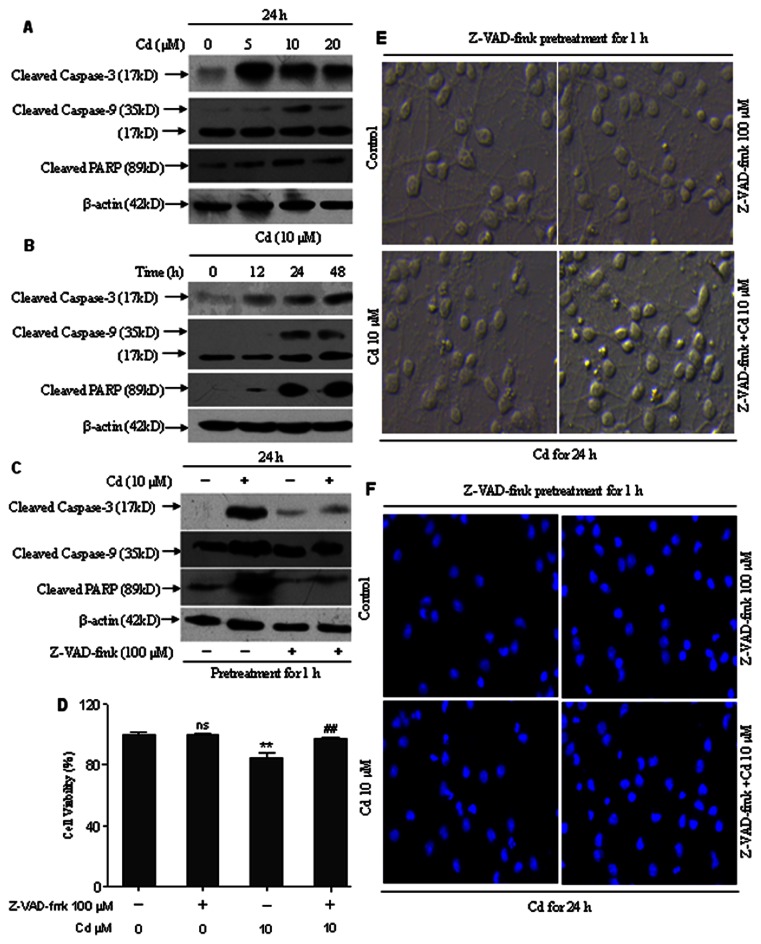
Figure 7. Cd induced neuronal apoptosis by caspase-dependent mechanism.
(A and B) Cd increased cleavage of caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP. Cells were exposed to 0–20 µM Cd for 24 h, or 10 µM Cd for 0–48 h and then analyzed by Western blotting. All experiments were performed twice. (C) A broad caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-fmk, reverses Cd-induced cleavage of caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP. Cerebral cortical neurons, treated with 10 µM Cd for 24 h following pretreatment with a pan caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-fmk (100 µM) for 1 h, were harvested. Cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting. All experiments were performed twice. (D) Z-VAD-fmk prevented cell death induced by Cd. Cell viability of cerebral cortical neurons treated with/without Cd (10 µM) in the presence or absence of Z-VAD-fmk (100 µM) for 12 h. Results are presented as mean± SD (n = 6). *Statistical significance between control and Cd treatment (5, 10 and 20 µM); #Statistical significance between cells cultured in the absence and presence of Z-VAD-fmk. ns Not significant; **P<0.01; ##P<0.01, using Student’s t-test. (E) Z-VAD-fmk prevented morphological alterations induced by Cd. Morphology of cerebral cortical neurons, treated with/without 10 µM Cd in the presence or absence of 100 µM Z-VAD-fmk for 24 h, was assessed using a LEICA inverted phase-contrast microscope (200×) equipped with digital camera. All experiments were performed twice. (F) Cd-induced apoptosis were suppressed by Z-VAD-fmk. Cells were pretreated with Z-VAD-fmk (100 µM) for 1 h, followed by treatment with 10 µM Cd for another 24 h to determine apoptosis by Hoechst 33258 staining under a fluorescence microscope (arrows, apoptotic cells). The original magnification is 200×. All experiments were performed twice.