Fig. 3. AEA and Virodhamine inhibit agonist-mediated GPR55E internalization.
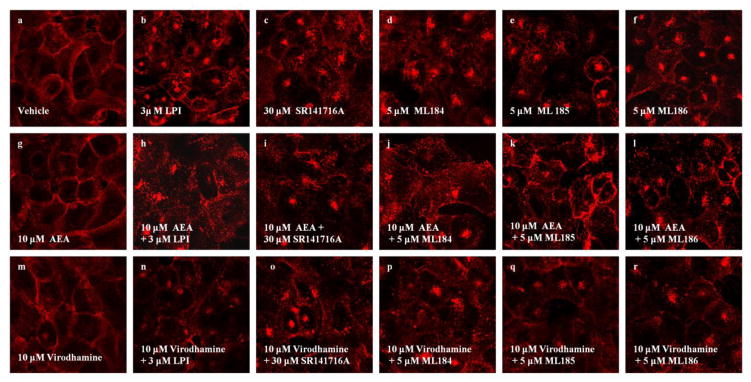
U2OS cells expressing HAGPR55E were pre-labeled with anti-HA antibody and Alexa Fluor 568 antibody. Cells were then pre-incubated with virodhamine (3 μM) for 15 min, followed by additional of 40 min incubation along with the agonist. Membrane staining was captured by confocal microscopy at 63x magnification. Upon treatment with vehicle (a) 10 μM AEA (g) and 10 μM virodhamine (m), cells show primarily membrane localization of GPR55. Treatment with 3 μM LPI (b), 30 μM SR141716A (c), 5 μM ML184 (d), 5 μM ML185 (e) and 5 μM ML186 (f), resulted in receptor internalization, evident by loss of plasma membrane receptor staining. Treatment with 10 μM AEA and 10 μM virodhamine largely attenuated receptor internalization induced by 3 μM LPI (h,n), 30 μM SR141716A (i,o), 5 μM ML184 (j,p), 5 μM ML185 (k,q) and 5 μM ML186 (l,r). Data are representative examples of at least three individual experiments.
