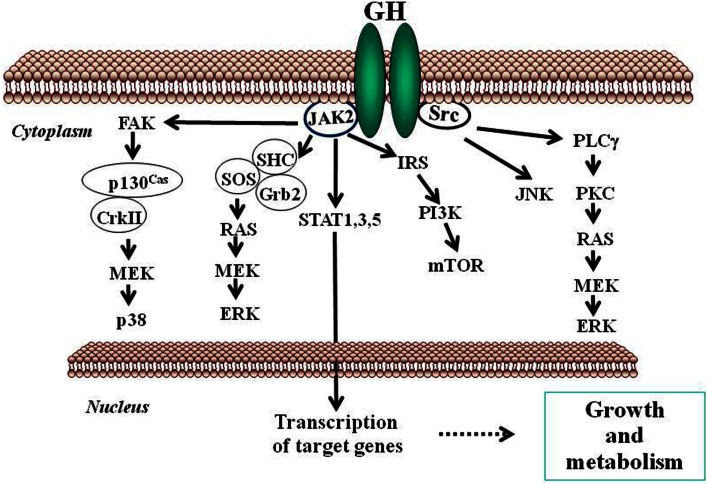
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of signaling pathways used by GH to regulate growth and metabolism. GH binds to a preformed GHR dimmer which results in activation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase bound to the receptor box 1 sequence proximal to the membrane. Simultaneously, Src kinase is also activated. Canonical protein-tyrosine kinase JAK2 signaling via STAT5 involves phosphorylation of key tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain of GHR, which bind the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain of STAT5a/b, recruiting STATs to the activated JAK2 and thus facilitating their tyrosine phosphorylation and subsequent dimerization through their SH2 motifs. Dimerized STAT5 translocates to the nucleus to regulate gene transcription. STAT1 and STAT3 undergo direct tyrosine phosphorylation by JAK2 without the requirement for receptor binding. ERK can be activated either by SRC and/or PLCγ and Ras, or by JAK2 via the adaptors SHC, GRB, and SOS. JNK is activated by SRC. The PtdIns 3-kinase and the serine-threonine-protein kinase mTOR pathway is activated by JAK2 via IRS phosphorylation. These signaling pathways influence, directly or indirectly, transcription of genes involved in growth and metabolism. ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; Grb, growth factor receptor-bound protein; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; JAK2, Janus kinase 2; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MEK, dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase Cγ; SHC, SH2-domain containing transforming protein; SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signaling; SOS, son of sevenless; SRC, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription.