Figure 5.
Truncation of the C Terminus in p110β Decreases Its Activity for Lipid Substrates and Increases ATP Hydrolysis in the Absence of Lipids
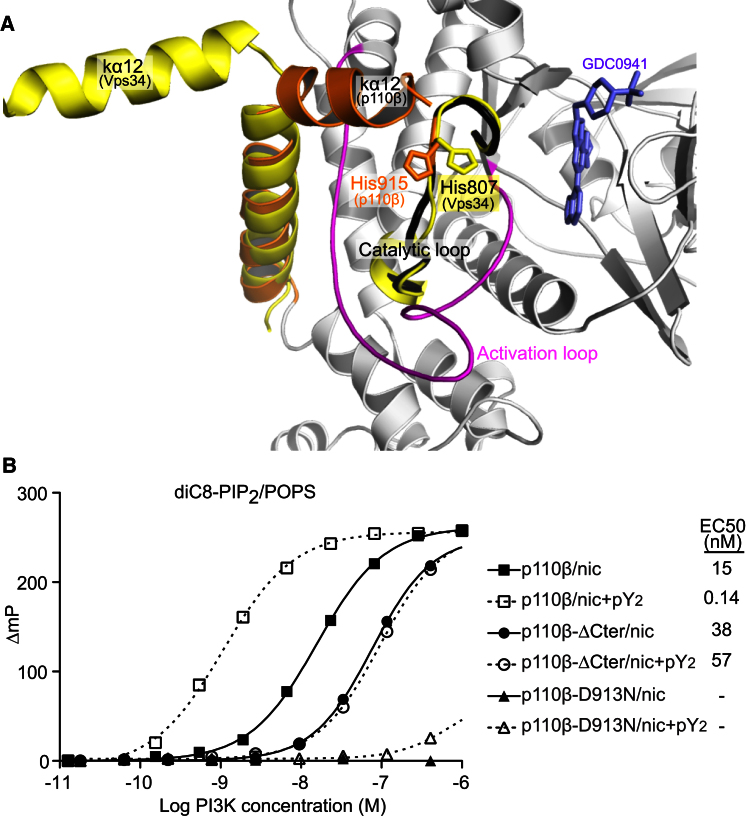
(A) The p110β kinase domain has the signatures of an inactive conformation: C-terminal Kα12 helix folds over the activation loop and His915 (from the DRH motif) points away from the active site (orange). They differ from the same elements in the presumably active conformation of Vps34 (yellow) (PDB: 2X6H).
(B) Lipid kinase activity (ADP formation) of the wild-type p110β/p85α, in comparison with a truncation mutant lacking 17 residues from the p110β C terminus (ΔCter) and a kinase-dead mutant (D913N). Activities were determined in the absence and presence of 10 μM PDGFR pY2. For the D913N mutant, the EC50 was too high to be determined accurately (y axis as in Figure 1B).