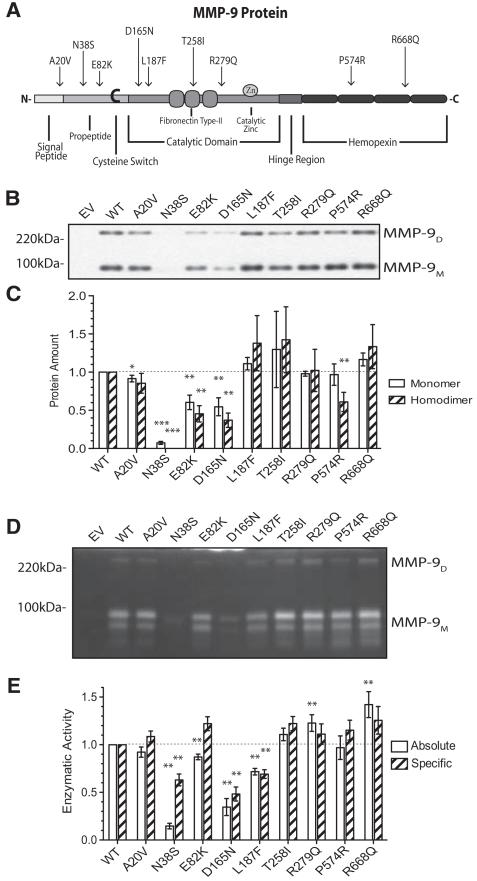
Figure 1.
Functional consequences of MMP-9 Exon SNPs. A, A cartoon of the MMP-9 protein denoting the various functional domains and the relative locations of the SNPs investigated resulting in amino acid changes. C indicates the cysteine switch, Zn the zinc binding site, and the various functional domains are indicated by the different shades. B, Nonreducing PAGE of the culture supernatants collected 24 hours after transfection of HEK293 cells with the denoted constructs. The membrane after transfer was blotted with anti–MMP-9 antibody (1:1000 in TBST containing 1% dry milk) and shows the upper and lower-MMP-9 immunoreactive bands corresponding to the dimeric and monomeric MMP-9 protein. C, A bar plot summary of densitometric analysis of monomeric (open bars) and dimeric (hatched bars) protein amount normalized by the respective values for the wild-type. D, Gelatin zymography of cell culture supernatant of transfected cells, as in B. The enzymatic activity was quantified by densitometric analysis of the gelatin zymography (see online-only Data Supplement Figure SI). E, Absolute (open bars) and specific (hatched bars) enzymatic activity normalized to that of the wt-MMP-9 transfected experiment (first columns). The enzymatic activity quantified is the total activity including both the monomeric and dimeric MMP-9 activity. Bar plots are mean±SEM from 5 independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 by Mann–Whitney nonparametric test. MMP-9 indicates matrix metalloproteinase-9; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; and HEK, human embryonic kidney.