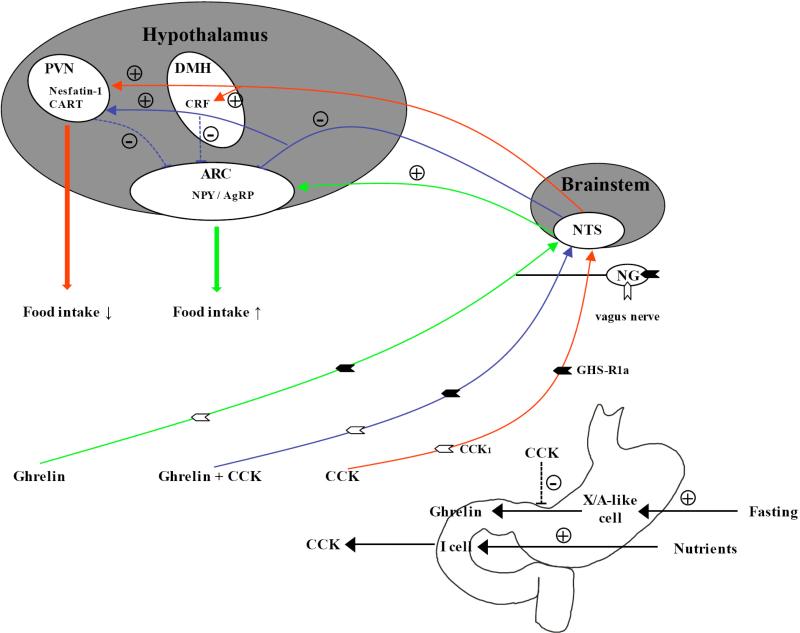
Fig. (1).
Interaction between ghrelin and CCK in the regulation of food intake. During fasting ghrelin is released from X/A-like cells of the gastric mucosa stomach and mediates its orexigenic effect via the afferent vagus nerve bearing the GHS-R1a and CCK1 receptors and activation of NPY/AgRP positive neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. CCK is released from the upper small intestine after nutrient exposure and reduces food intake by activating central neurons containing anorexigenic mediators such as CRF, CART and nesfatin-1. When injected simultaneously with ghrelin, CCK blocks the ghrelin induced food intake most likely by inhibiting ghrelin stimulated neuronal activation in the arcuate nucleus. CCK also reduces circulating ghrelin levels. + stimulation; - inhibition; ↑ increase; ↓ decrease; dotted line, potential pathways; AgRP, Agouti-related peptide; ARC, arcuate nucleus; CRF, corticotropin-releasing factor; DMH, dorsomedial nucleus of the hypothalamus; NG, nodose ganglion; NPY, neuropeptide Y; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; PVN, paraventricular nucleus. References: [40, 147-151, 170, 171]