Figure 9.
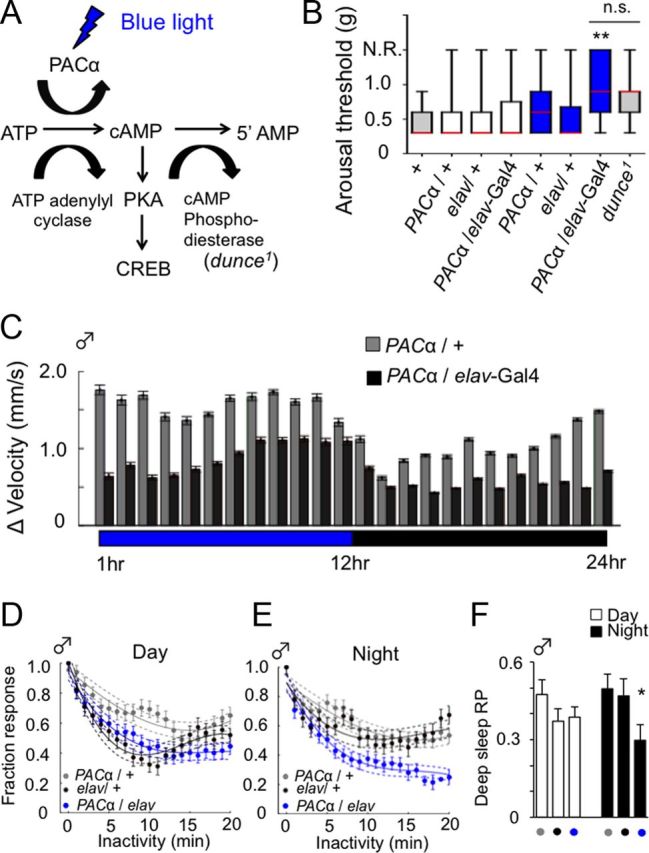
Adenylyl cyclase activity increases nighttime sleep intensity. A, cAMP synthesis and degradation pathway. A transgenic adenylyl cyclase (PACα) is activated by blue light, resulting in increased levels of cAMP and consequent plasticity signaling mechanisms (PKA and CREB). Increased cAMP levels are also achieved by the phosphodiesterase gene mutation, dunce1. B, Acute blue light activation of PACα increases arousal thresholds to levels similar to dunce1 mutants. Arousal thresholds (the minimal vibration, g, required to arouse a quiescent fly; see Materials and Methods) for wild-type (+, n = 42), UAS-PACα/+ (n = 36), elav-Gal4/+ (n = 34), UAS-PACα/elav-Gal4 (n = 37), and dunce1 (n = 71). White boxplots indicate white light exposure; blue boxplots, 10 min blue light exposure. **p < 0.01 by Kruskal-Wallis comparison of medians (red) adjusted for multiple comparisons. C, Baseline and stimulus-induced velocity (± SEM) for UAS-PACα/+ control male flies and UAS-PACα/elav-Gal4 male flies in response to hourly stimulation by 1.2 g for 72 h averaged over a 24 h period. Blue light (458 ± 10 nm) was turned on throughout the day and turned off at night for both. D, E, Acute activation of PACα with blue light during the day increases sleep intensity at night in males. The sleep intensity profiles for UAS-PACα/+ (gray, n = 85), elav-Gal4/+ (black, n = 85), and the blue-light-activated UAS-PACα/elav-Gal4 (blue, n = 85) is shown (± SEM). Third-order polynomials were fitted to normalized, smoothed mean responsiveness data for the first 20 min of inactivity for daytime or nighttime sleep. Day: UAS-PACα/+, r2 = 0.85; elav-Gal4/+, r2 = 0.84; UAS-PACα/elav-Gal4, r2 = 0.97. Night: UAS-PACα/+, r2 = 0.88; elav-Gal4/+, r2 = 0.77; UAS-PACα/elav-Gal4, r2 = 0.94. F, Deep sleep response probability (RP) data and statistics. *p < 0.05 by Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
