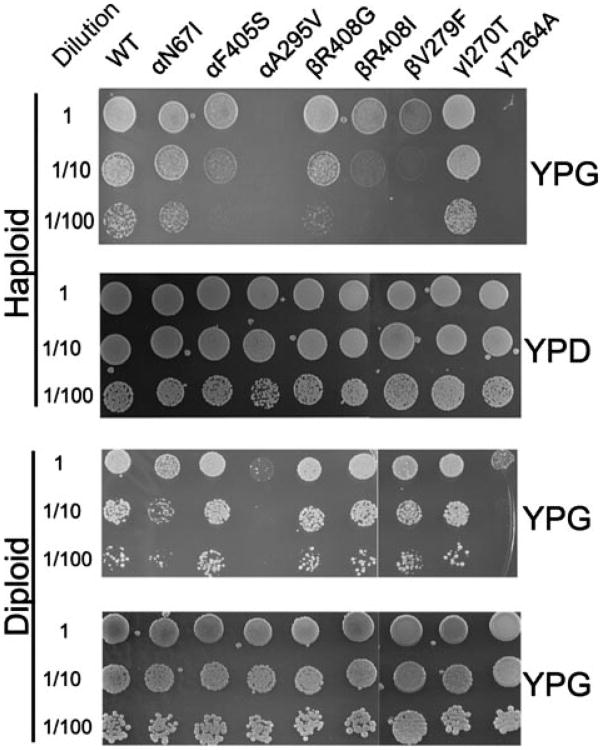
Figure 2. Growth phenotype of the yeast strains with the mgi mutations.
The wild type and mutant yeast strains were grown on YPD and YPG at 30 °C at 3 dilutions, as indicated. The haploid cells were mated to the wild type strain, K289-3A (21), and a diploid cell selected and tested for growth in the same manner. Thus, the diploid strain is heterozygous, whereas the haploid strain is homozygous, for the mgi mutation.