Figure 1.
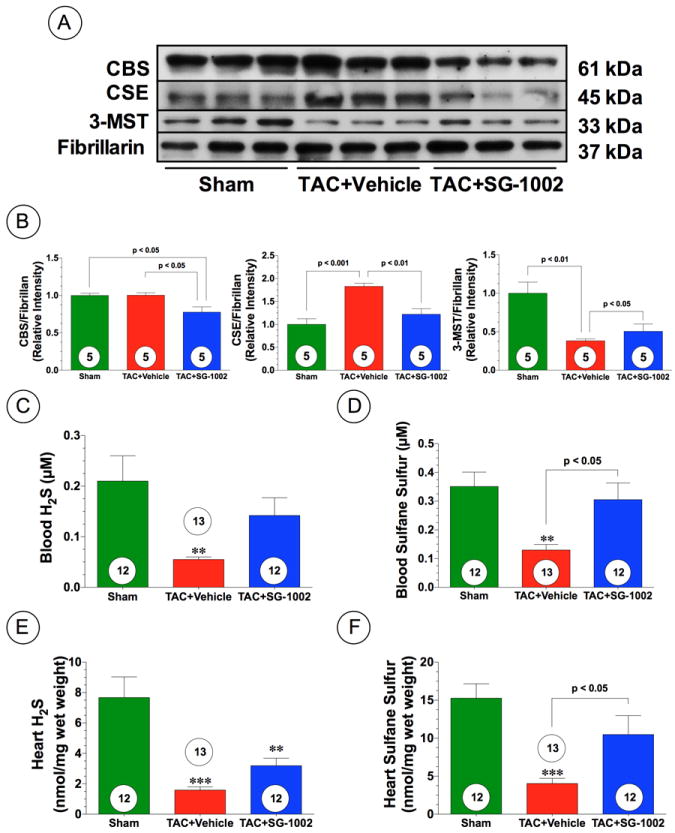
Heart failure reduces sulfide levels in mice. (A-B) Representative immunoblots and densitometric analysis of cystathionine gamma lyase (CSE), cystathionine beta synthase (CBS), and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfutransferase (3-MST) in the hearts of Sham, TAC+Vehicle, and TAC+SG-1002 treated mice at 6 weeks of TAC. (C-D) Circulating levels of free H2S and sulfane sulfure after 6 weeks of pressure overload-induced heart failure (TAC) in groups of mice maintained on a standard chow (TAC+Vehicle) or maintained on a chow containing the H2S donor SG-1002 (TAC+SG-1002, 20 mg/kg/day). (E-F) Myocardial levels of free H2S and sulfane sulfur in the experimental groups. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM. Numbers in bars represent the sample size. **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 vs. Sham.
