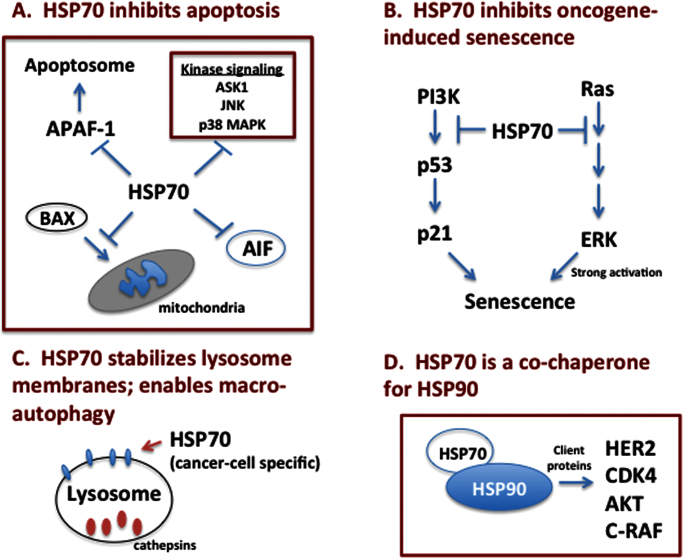
Fig. 3.
Cancer-relevant pathways affected by HSP70. (A) HSP70 inhibits the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis pathways, by inhibiting BAX translocation to mitochondria, the recruitment of APAF-1 to the apoptosome, the activity of stress-induced kinases and the function of AIF-1. (B) HSP70 inhibits both p53-dependent and -independent senescence. (C) HSP70 localizes to lysosome membranes specifically in cancer cells, stabilizes lysosome function and allows for autophagy, a key cancer survival pathway. (D) HSP70 is an obligate co-chaperone for HSP90 and is essential for the proper folding and function of HSP90 chaperone proteins like HER2, AKT, CDK4 and C-RAF.