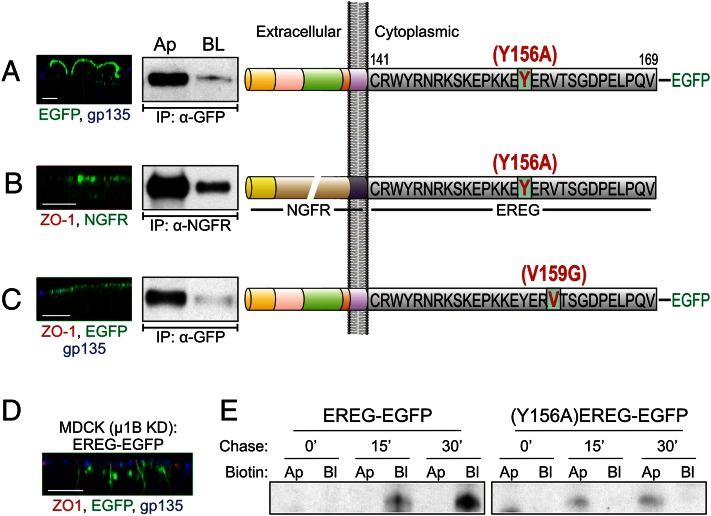
Fig. 2.
Basolateral localization of EREG is AP-1B–independent but depends on a YXXΦ-based basolateral motif for regulation of its biosynthetic delivery. (A) EREG-EGFP constructs were mutated at Tyr-156 to alanine. (Right) The resulting (Y156A)EREG-EGFP was stably expressed and examined in polarized MDCK cells. (Left) Confocal xz projections showing EREG (green) and gp135 (blue) localization. (Center) Selective cell surface biotinylation. (B) The Y156A mutation was introduced into the NGFR-EREG CT chimera shown in Fig. 1C; the resulting chimera [NGFR-(Y156A)EREG CT] was stably expressed in polarized MDCK cells. Confocal projections in the xz plane (Left) and selective cell surface biotinylation (Center) are shown. (C) EREG-EGFP constructs were mutated at Val159 to Gly (occupying the Φ position in the YXXΦ motif); the resulting (V159G)EREG-EGFP was stably expressed and examined in polarized MCDK cells. Confocal and biotinylation data from these cells are shown as in A. (D) Parental MDCK cells with stable µ1B knockdown were transfected with EREG-EGFP constructs and polarized on Transwell filters. The xz confocal projections show GFP fluorescence (green) along with immunostaining for ZO-1 (red) and gp135 (blue). (E) Polarized EREG-EGFP and (Y156A)EREG-EGFP MDCK cells were pulse-labeled for 20 min and then chased for the indicated times. After the pulse-chase, cells were biotinylated on either the apical (Ap) or basolateral (BL) cell surfaces and lysed. Lysates were sequentially immunoprecipitated with GFP antibody, followed by affinity purification with streptavidin agarose beads. Lysates were subsequently resolved on SDS/PAGE (8–12% gradient) and dried, and autoradiographs were developed. These radiographs show the newly synthesized cell surface EREG species at the indicated chase times.