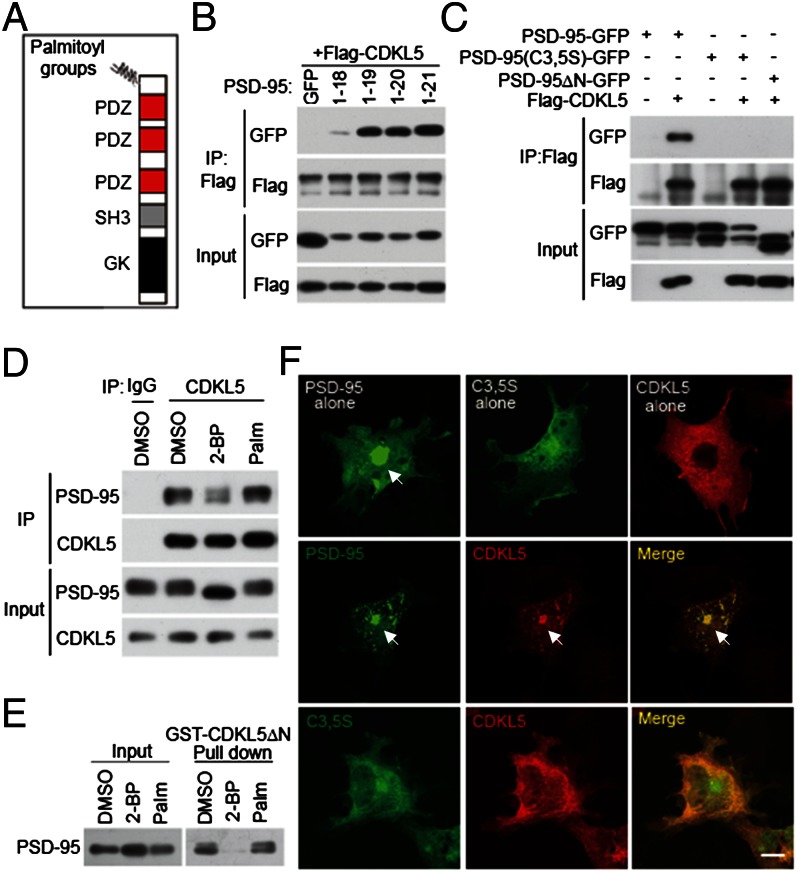
Fig. 2.
The CDKL5–PSD-95 interaction is controlled by palmitoylation. (A) Schematic diagram for domain structures of PSD-95. (B) Determination of the minimal binding region for CDKL5 in PSD-95. GFP or GFP-tagged PSD-95 derivatives (amino acids 1–18, 1–19, 1–20, and 1–21) were cotransfected with Flag-CDKL5 into 293T cells. Coimmunoprecipitation was performed in cell lysates with a Flag antibody. (C) Mutations preventing palmitoylation of PSD-95 abolish its interaction with CDKL5. PSD-95-GFP, PSD-95 (C3,5S)-GFP, and PSD-95ΔN-GFP were transfected individually or together with Flag-CDKL5 into 293T cells. Coimmunoprecipitation was performed in cell lysates with a Flag antibody. (D) Inhibition of palmitoylation decreases the interaction of CDKL5 with PSD-95 in neurons. Cortical neurons were treated with vehicle (DMSO), 20 μM 2-BP, or 20 μM palmitate for 8 h. After treatment, cells were harvested and the lysates were immunoprecipitated with a CDKL5 antibody. (E) GST pull-down experiment showing that the interaction of CDKL5 with PSD-95 is palmitoylation-dependent. Cortical neurons were treated as in D and the lysates were incubated with GST or GST-CDKL5ΔN affinity beads. Total lysates and precipitates were immunoblotted for PSD-95. (F) Palmitoylation-dependent interaction of CDKL5 and PSD-95 in COS-7 cells. COS-7 cells were transfected with PSD-95-GFP, PSD-95 (C3,5S)-GFP, and Flag-CDKL5, individually or together. Cells were fixed and stained for Flag. Arrows indicate the accumulation of proteins at the perinuclear region. (Scale bar: 20 μm.)