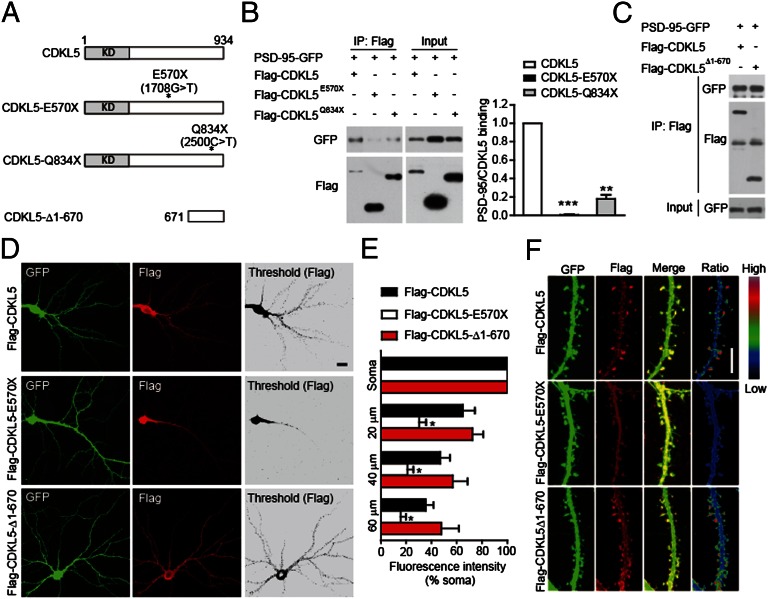
Fig. 4.
Disease-associated mutations impair the interaction of CDKL5 with PSD-95 and its synaptic localization. (A) Schematic diagram showing the structures of CDKL5 and its mutants. KD, kinase domain. (B) Mutations E570× and Q834× impair the interaction of CDKL5 with PSD-95. The interaction was assayed by coimmunoprecipitation in 293T cells coexpressing GFP-tagged PSD-95 and Flag-tagged CDKL5 or its mutants. n = 3; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (C) Interaction of CDKL5 C-terminal region (CDKL5-Δ1-670) with PSD-95 assayed by coimmunoprecipitation. Subcellular localization of Flag-tagged CDKL5 and its mutants. (D) Representative images of neurons transfected with Flag-tagged CDKL5 or its mutants together with GFP, and stained for GFP and Flag. (Scale bar: 20 μm.) (E) Quantitation of average fluorescence in cell soma and in dendritic segments at the indicated distances from the soma in neurons expressing Flag-tagged proteins. n = 5–6 neurons for each condition; *P < 0.05 compared with Flag-CDKL5. (F) Representative images of dendrites showing the localization of Flag-tagged proteins in dendritic segments of transfected neurons. Ratio images indicate their enrichment in dendritic spines. (Scale bar: 5 μm.)