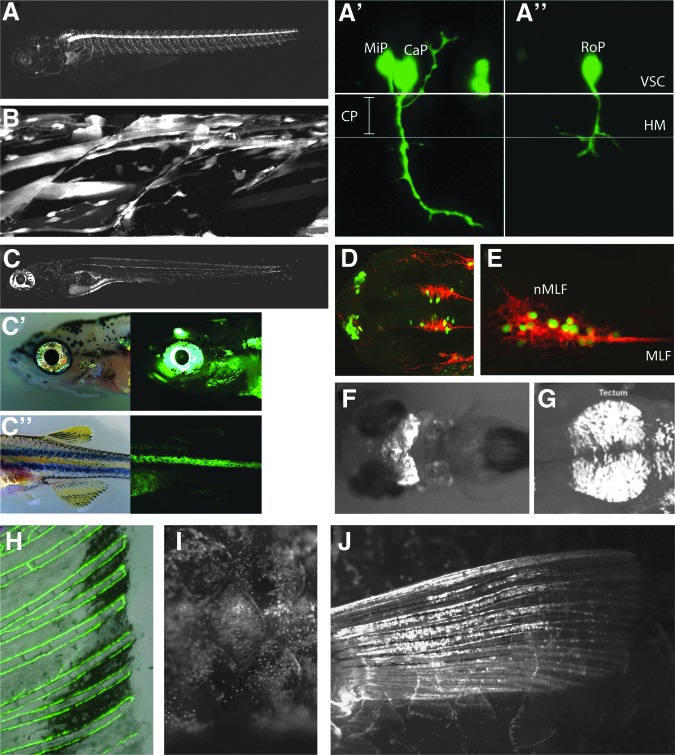
FIG. 1.
GFP expression of selected Tuebingen driver lines (TDL). (A, A′, A″) TDL6 marking primary motorneurons in larval zebrafish embryos with (A) shows a larva at 5 dpf and (A′,A″) showing detailed GFP expression at 24 hpf with middle (MiP) and caudal primary motorneuron (CaP) being labeled in A′, and the rostral primary motorneuron (RoP) being labeled in A″. (B) TDL42 labels the myogenic lineage, from myoblasts to differentiated muscle fibers. Shown is a confocal projection of two dorsal myotomes of the midtrunk of a 3 dpf larva. (C, C′, C″) TDL358 gives GFP expression in iridophores, glia of the lateral line system, and the pineal gland. (C) shows a larva at 5 dpf, with iridophores labeling being most pronounced in iridophores of the eyes and in the ventral and yolk sac stripe. Schwann cells wrapped around the lateral line nerve are visible along the horizontal myoseptum. (C′, C″) In juveniles at 30 dpf, GFP expression is most apparent in iridophores of the eyes and the first interstripe. (D) Dorsal view of a 28 hpf TDL354-line embryo combined with immunohistochemistry for the neuronal marker zn-12 (HNK1). The TDL354 line shows expression in primary neurons of the forebrain belonging to the dorso-rostral cluster (drc) and in a subset of nMLF (nucleus of the medial longitudinal fasciculus) neurons located in the ventral midbrain. (E) Lateral view of the ventral midbrain of a 28 hpf TDL235-line embryo co-stained with zn-12. Neurons belonging to the nMLF are GFP positive. (F) TDL234 shows GFP expression in the midbrain at 3 dpf. (G) In TDL318-line 28 hpf embryo, cells are labeled in the dorsal midbrain in the region of the forming tectum. (H) TDL244-3 results in GFP expression in the vasculature, here shown in the adult caudal fin. (I) TDL22 shows GFP expression in the scales of the adult zebrafish. (J) TDL74 labels the pectoral fins of the adult zebrafish.