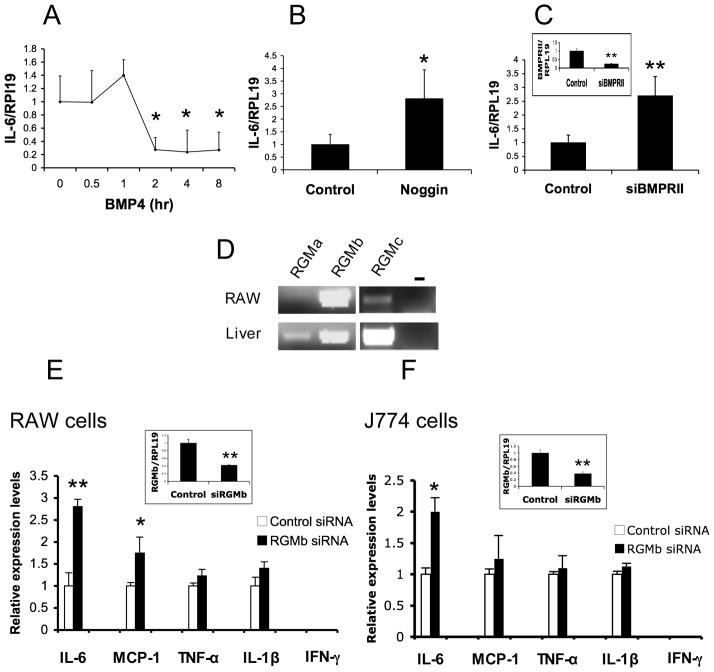
Figure 1.
IL-6 is a target of Dragon in RAW264.7 and J774 macrophages. (A, B and C) IL-6 mRNA expression is inhibited by BMP4 (A), and increased by noggin (B) or by inhibition of BMPRII expression (C). RAW264.7 macrophages were incubated with BMP4 (50 ng/ml) for 0–8 hrs, or incubated with noggin (500 ng/ml) overnight, or transfected with control or BMPRII siRNA. Cells were then harvested for RNA extraction and real time PCR for IL-6 and RPL19. IL-6 expression levels of the treated cells were expressed as a fraction of values from the controls. (D) Expression of RGMa, RGMb and RGMc mRNAs in RAW264.7 macrophages. Total RNA from RAW cells was extracted for RT-PCR to determine the expression of RGMa, RGMb and RGMc. Total RNA from the mouse liver was used in PCR analyses as positive controls. (E and F) IL-6 mRNA expression is up regulated by inhibition of Dragon expression in RAW264.7 (E) and J774 (F) macrophages. RAW264.7 (E) or J774 (F) cells were transfected with control or Dragon siRNA, and analysed for mRNA levels of IL-6, MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-1β, IFN-γ and Dragon. The expression levels of these factors are normalized to RPL19 and expressed as a fraction of values from the respective controls. The efficacy of BMPRII siRNA or Dragon siRNA was shown in the insets. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.