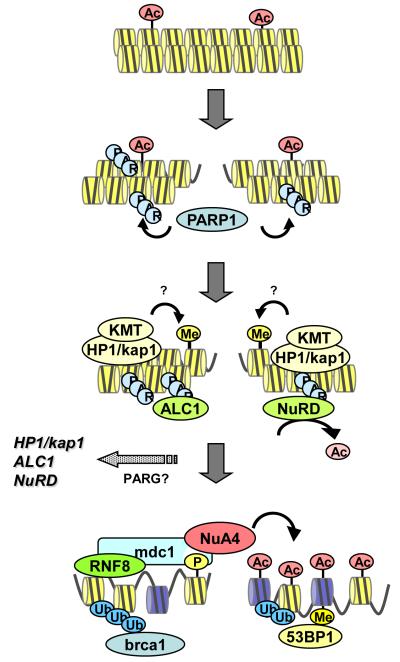
Figure 4. Creating access to Double strand Breaks.
Chronological sequence of steps in remodeling of a double strand break (DSB). Initial polyADP-ribosylation (PARylation) by PARP1 leads to rapid recruitment of NuRD and ALC1 (through interaction with PAR) and Kap-1/HP1 complexes (possibly through interaction with PAR). Deacetylation (by NurD) and proposed H3K9 methylation by lysine methyltransferases (KMTs), including suv39h1 and G9a, creates a temporary repressive chromatin structure. Subsequent phosphorylation (P) of γH2AX recruits NuA4-Tip60, promoting the ordered remodeling of the chromatin through H2A.Z exchange, histone acetylation (Ac) and chromatin ubiquitination (Ub). This creates a common chromatin template for DSB repair by either nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) -or homologous recombination (HR)-mediated repair._ KMT, lysine methyltransferases.