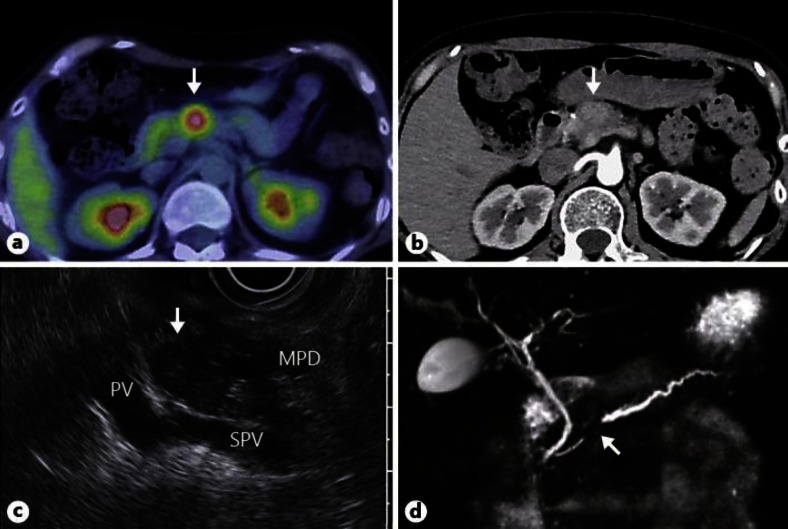
Fig. 2.
Imaging diagnosis of a solitary tumor in the pancreatic body. a PET/CT showing abnormal uptake in pancreatic body (max. standardized uptake value, 3.1) (arrow). b Enhanced abdominal CT in the arterial phase, showing a faintly attenuating 20-mm round mass in the pancreatic body (arrow). c EUS revealing a well-circumscribed hypoechoic mass in the pancreatic body and accompanying upstream pancreatic duct dilatation (arrow). PV = Portal vein; SPV = splenic vein; MPD = main pancreatic duct. d MRCP reveals stenosis of the main pancreatic duct at the pancreatic body and dilated upstream pancreatic ducts (arrow).