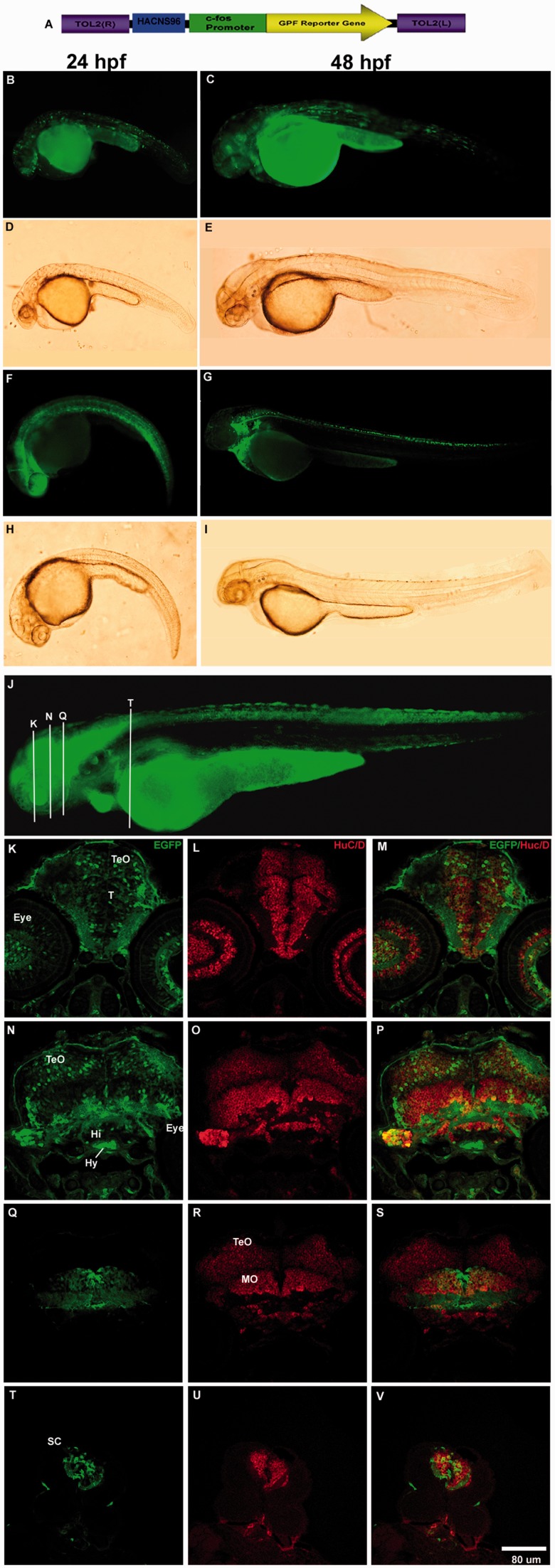
Fig. 4.
HACNS96 drives EGFP expression to the developing nervous system in stable and transient transgenic zebrafish lines at 24, 48, and 72 hpf. (A) Diagram of the transgene structure based on the Tol2 system. Fluorescent (B, C, F, and G) and bright field (D, E, H, and I) photomicrographs of selected whole mount transient or stable transgenic zebrafish embryos expressing the reporter protein EGFP under control of the human HACNS96 sequence at 24 hpf (B, D, F, and H) and 48 hpf (C, E, G, and I). (J) Representative transgenic zebrafish expressing EGFP under the control of HANCS96 at 72 hpf where white bars indicate approximately the location of coronal cryostat sections showing a detail of the EGFP expression pattern (K, N, Q, and T), cells expressing the early neuronal marker HuC/D (L, O, R, and U) and the resulting overlay (M, P, S, and V). TeO, tectum opticum; T, midbrain tegmentum; DT, dorsal tegmentum; Po, preoptic region; MO, medulla oblongata; OC, otic capsule; SC, spinal cord; Hi, hypothalamus; Hy, hypophysis.