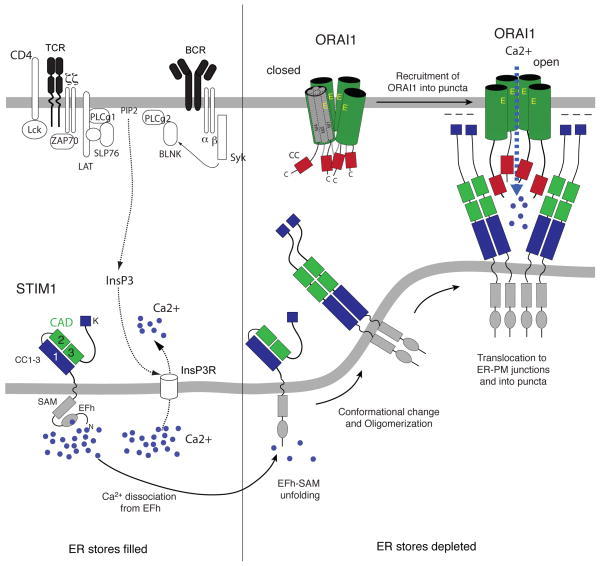
Figure 2. The molecular choreography of CRAC channel activation.
In resting lymphocytes, ER Ca2+ stores are filled with Ca2+ bound to the EF hand Ca2+ binding domain in the N-terminus of STIM1. Antigen receptor stimulation causes the activation TCR/BCR-proximal signalling cascades and the production of InsP3, resulting in the release of Ca2+ from the ER through InsP3 receptors, which are non-selective ion channels. The fall in ER Ca2+ concentration leads to the dissociation of Ca2+ from the EF hand domain in STIM1, unfolding of the STIM1 N-terminus and the multimerization of STIM1 proteins 6. STIM1 multimers translocate to junctional ER sites in which the ER membrane is juxtaposed to the plasma membrane. STIM1 multimers form large clusters (or puncta) into which they recruit ORAI1 CRAC channels. A minimal CRAC channel activation domain (variously referred to as the CAD, SOAR, OASF or CCb9 domain) in the C terminus of STIM1 (green boxes) is necessary and sufficient for ORAI1 binding, CRAC channel activation, and SOCE 29, 184, 186, 187. This domain contains two coiled (CC) domains, which interact with a CC domain in the C-terminus (red boxes) and additional domains in the N-terminus (not shown) of ORAI1 27. Abbreviations: SAM, sterile-alpha motif.