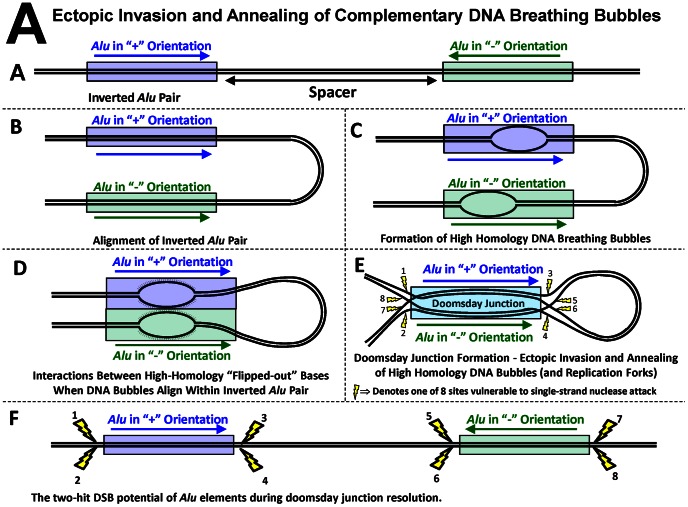
Figure 1. Proposed mechanism for formation and resolution of doomsday junction formed by ectopic invasion and annealing of complementary DNA breathing bubbles.
(A) Two Alu elements in opposite orientations form an inverted Alu pair. (B) These inverted Alu pairs can align as high-homology regions. (C) DNA bubbles create short-lived sections of single-stranded DNA [25]. (D) The unbound bases within these bubbles are characterized by their flipping out from the centerline of the DNA strand [24]. Coincident passage of these bubbles within aligned Alu elements can create the opportunity for interactions between the flipped-out bases of the complementary DNA strands. (E) The ectopic invasion and annealing of single-stranded DNA associated with high-homology DNA bubbles could potentially extend to the entire length of the Alu elements. The hypothetical conformation created by this interaction is termed a doomsday junction. A similar interaction may also occur between high-homology replication forks and is described in Figure S1 and [18]. Eight segments of single-stranded DNA formed at the boundary of doomsday junctions create the opportunity for single-strand nuclease attack. These sites are illustrated as yellow lightning bolts. (F) As again illustrated by the yellow lightning bolts, each end of each Alu element involved in the doomsday junction is vulnerable to a double-strand break. This two-hit hypothesis for each Alu element was incorporated into the model's algorithm (see text).