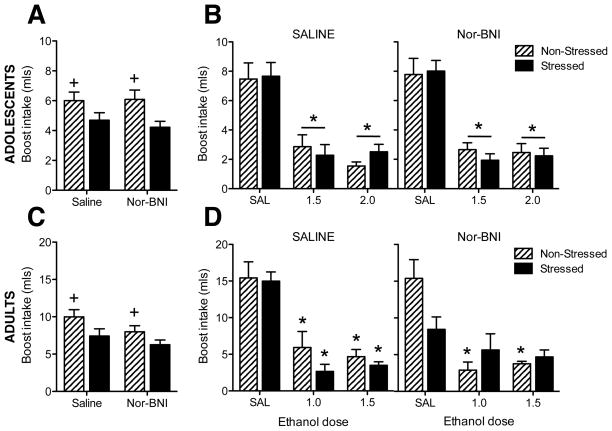
Fig 1. Ethanol-induced conditioned taste aversion.
(A) Adolescent conditioning day Boost intake. Non-stressed rats consumed more Boost than stressed rats (indicated by +), regardless of pretreatment condition. (B) Adolescent test day Boost intake. Both doses of ethanol elicited aversions (indicated by *), regardless of stress or pretreatment condition. (C) Adult conditioning day Boost intake. Non-stressed rats consumed more Boost than stressed rats (indicated by +), regardless of pretreatment condition. (D) Adult test day Boost intake. Among non-stressed rats, both doses of ethanol elicited conditioned taste aversions regardless of pretreatment condition (indicated by *). Among stressed adults, saline-pretreated rats demonstrated aversions to both ethanol doses (indicated by *) whereas rats pretreated with nor-BNI did not exhibit aversions to any ethanol doses.