Fig 2. U62,066-induced conditioned taste aversion.
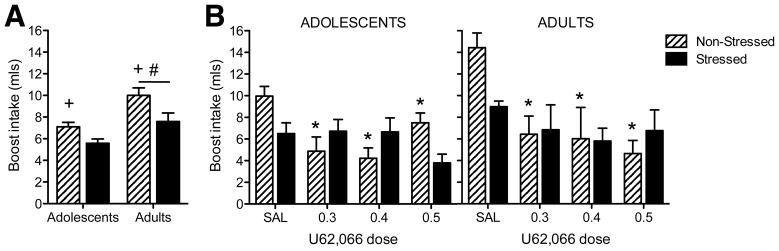
(A) Conditioning day Boost intake. Non-stressed rats consumed more Boost than stressed rats (indicated by +), with adults consuming more Boost than adolescents (indicated by #). (B) Test day Boost intake. Regardless of age, all doses of U62,066 elicited conditioned taste aversions in non-stressed subjects (indicated by *) whereas no aversions were evident in stressed animals.
