Figure 1.
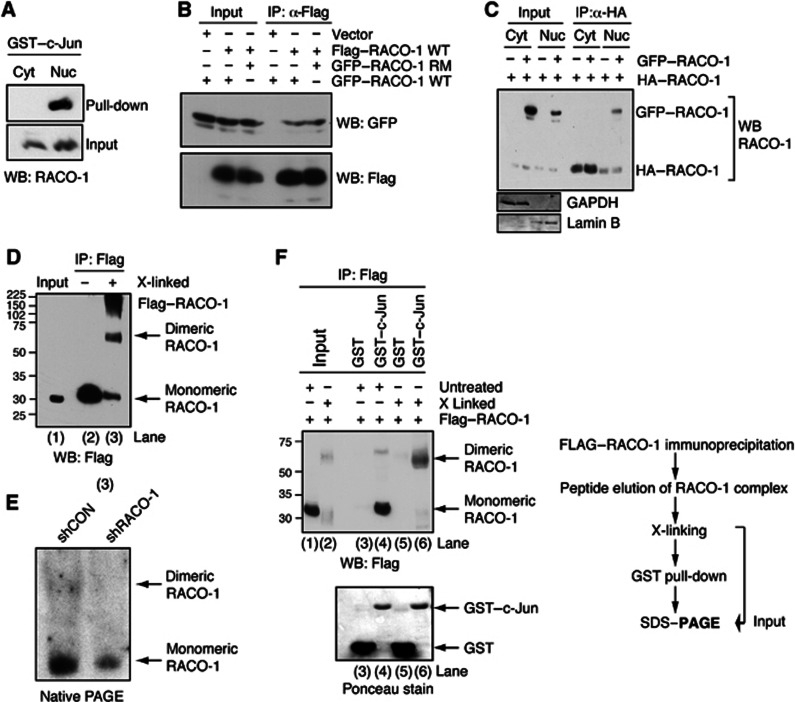
c-Jun binds to nuclear dimeric RACO-1. (A) Nuclear but not cytoplasmic RACO-1 interacts with recombinant c-Jun. RACO-1-transfected cells were fractionated into cytoplasmic/nuclear extracts prior to incubation with GST–c-Jun. (B) RACO-1 homodimerises independently of the RING domain. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag–RACO-1 and GFP–RACO-1 wild-type (WT) or RING mutant (RM). Flag–RACO-1 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates and associated GFP–RACO-1 detected by immunoblotting. (C) Nuclear but not cytoplasmic RACO-1 forms dimers. Transfected cells were fractionated into cytoplasmic/nuclear extracts prior to immunoprecipitation with α-HA-agarose beads. Associated GFP–RACO-1 was detected by immunoblotting. Immunoblotting for GAPDH and Lamin B validates the purity of subcellular fractionation. (D) RACO-1 forms dimers in vivo. Flag–RACO-1-transfected cells were immunoprecipitated, peptide eluted and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde (X-linked) before resolving by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotting with Flag antibody. (E) Endogenous RACO-1 forms a homodimer. Cell extracts from H727 cells, with stably integrated shLuciferase or shRACO-1, were analysed in nondenaturing PAGE and immunoblotted with RACO-1 antibody. (F) Recombinant c-Jun preferentially interacts with dimeric RACO-1. Cells were experimentally prepared as in (D). After chemical crosslinking, one-tenth of the eluate was removed to assess efficiency of crosslinking (lanes 1 and 2), and the remaining elution was either incubated with GST–c-Jun or GST as control (lanes 3–6). RACO-1 protein associated with GST–c-Jun was resolved by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.