Figure 6.
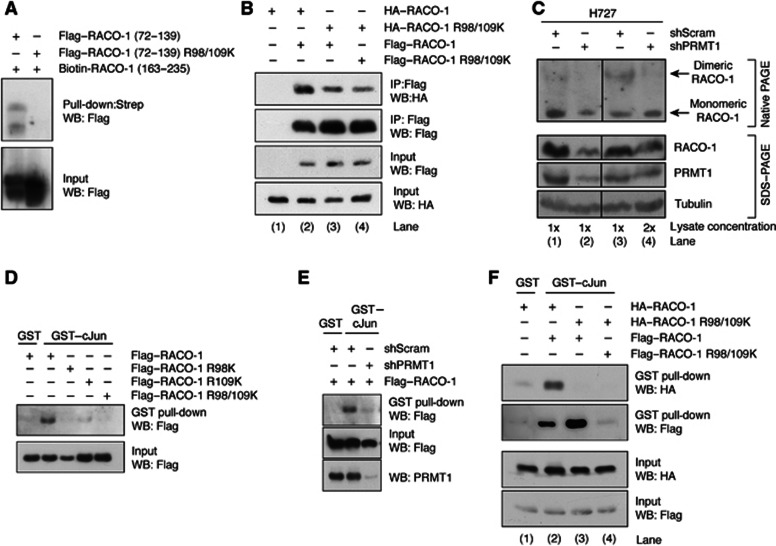
Methylation of RACO-1 by PRMT1 on R98 and R109 is required for dimerisation and c-Jun interaction. (A) Intramolecular interaction requires methylation on arginine 98 and arginine 109. Lysates from Flag–RACO-1 (72–139) or Flag–RACO-1 (72–139) R98/109K-expressing cells were incubated with a biotinylated RACO-1 peptide corresponding to residues 163–235. RACO-1-associated proteins were resolved by SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with α-Flag antibody. (B) Mutation of methyl arginine residues on one RACO-1 monomer is sufficient to disrupt dimer formation. Cells were transfected as in the Figure, Flag–RACO-1 immunoprecipitated and associated HA–RACO-1 detected by immunoblotting. (C) Silencing of PRMT1 suppresses endogenous RACO-1 dimer formation. Stable H727 cell lines expressing scrambled or PRMT1 silencing constructs were generated, and endogenous RACO-1 dimers detected by nondenaturing PAGE (top panel). However, denaturing SDS–PAGE analysis using equivalent lysates demonstrates that silencing of PRMT1 reduces RACO-1 protein levels (bottom panel, compare lanes 1 and 2). Subsequently, to normalise RACO-1 expression levels, the right-hand panel depicts results when twice the concentration of lysate is used (compare lanes 3 and 4). Hence, RACO-1 and PRMT1 expression levels are equivalent in lanes 3 and 4, but the appearance of dimeric RACO-1 is reduced. (D) Mutation of one methyl arginine residue on RACO-1 is sufficient to disrupt c-Jun binding. Cells were transfected with various RACO-1 methyl mutants and cell lysates incubated with GST–c-Jun. Associated Flag–RACO-1 was detected by immunoblotting. (E) Silencing of PRMT1 prevents RACO-1 from binding to c-Jun. (F) Methylation-induced dimer formation is required for binding of RACO-1 to c-Jun. Lysates derived from cells transfected as depicted in the Figure were incubated with GST–c-Jun and associated RACO-1 detected by immunoblotting for HA or Flag tag.
Source data for this figure is available on the online supplementary information page.