Fig. 1.1.
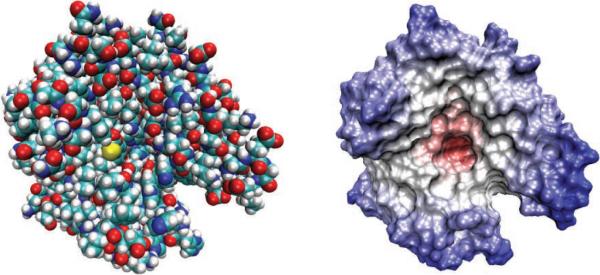
Molecular surfaces of the carbonic anhydrases-II [125]. (Left) The van der Waals (vdW) surface of the domain composed of the sum of overlapping vdW spheres. (Right) The solvent accessible surface (SAS) generated by rolling a small sphere on the vdW surface. In the macroscopic theory, the molecular domain inside the surface is given a low dielectric constant and the enclosed atoms are treated explicitly, while the exterior domain is treated as a homogeneous continuum medium with a higher dielectric constant. Poisson–Boltzmann models often use the SAS to define the molecular boundary, while generalized Born methods usually take the vdW surface.
