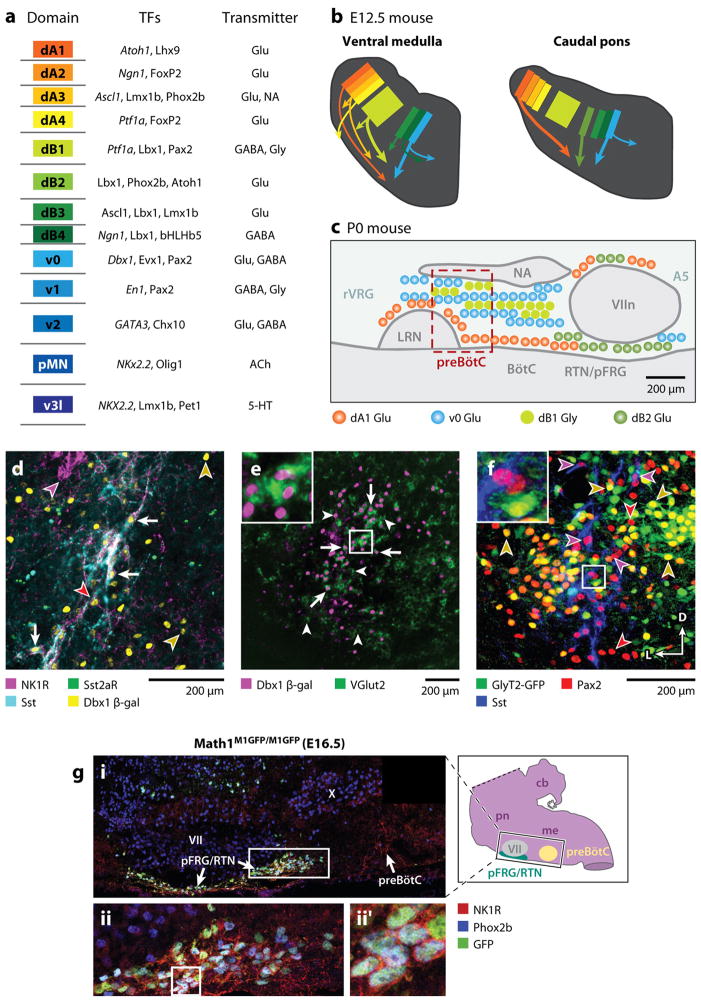
Figure 5. Genetic organization of brainstem respiratory regions.
A. Schematized description of brainstem progenitor domains for 8 dorsal (dA1–dB4) and 5 ventral progenitor populations (left) based on their relative location within brainstem progenitor region. Partial list of transcription factors expressed at some point within progenitors (italics) or post-mitotic neurons within each domain (middle). Neurotransmitter(s) identity of neurons derived from each domain. Adapted from (Gray 2008) B. Cartoon showing partial migratory path of ventral medulla (left) and caudal pons (right) neurons in embryonic mouse brainstem. Colors correspond to domains in (A). Thick arrows correspond to populations important for breathing. Note dB2 population (light green) is present only in caudal pons. C. Cartoon of developmental origin and approximate anatomical locations of respiratory-related populations in sagittal plane within ventral medulla and caudal pons. Colors correspond to developmental progenitor domain from A. Legend describes transmitter released by these neurons. Within the ventral respiratory column, nearly all respiratory-related glutamatergic neurons are Dbx1-derived. Magenta box outlines the location of preBötC SST-expressing neurons. RTN/pFRG, in contrast, contains Dbx1, Atoh1, and Phox2b glutamatergic populations. Ventral medulla also contains a large number of dB1 derived glycinergic neurons. B. PreBötC neurons are derived from Dbx1-expressing progenitors. Four color confocal image showing coexpression of NK1R (magenta), SST2aR (green), SST (cyan), and β-gal (yellow) in P0 Dbx1 β-gal mouse (adapted from (Gray et al 2010). Arrows indicate coexpression of all 4 genes. Images to right show single channel expression. Red arrowhead indicates Dbx1-derived NK1R/SST2aR-expressing neuron that lacks SST. Yellow arrowheads indicate Dbx1 derived neurons lacking coexpression. Magenta arrowhead indicates NK1R expressing nucleus ambiguus neuron. E. preBötC Dbx1 neurons are glutamatergic. Image showing β-gal (magenta) expression within the majority of VGlut2 (green) expressing preBötC neurons (adapted from (Gray et al 2010)). Inset is enlarged from central square. F. preBötC contains glycinergic neurons. Three color confocal image showing Pax2 (red) and Sst (blue) immunoreactivity with intrinsic GFP from a P0 GlyT2-GFP transgenic mouse (Morgado-Valle et al 2010). Arrows show Pax2 co-localization with Sst or GFP but no GFP expression in SST neurons. Inset is enlarged from central square. Scale bars = 200 μm. D – dorsal, L – lateral. G. RTN/pFRG Phox2b neurons express Phox2b and Atoh1. (A) Magnification of ventral respiratory column from E16.5 Math1M1GFP/M1GFP hindbrain, as indicated by the black rectangle on inset model hindbrain (black ventral region is pFRG/RTN while yellow circle indicates preBötC), showing NK1R (red), Phox2b (blue), and Math1-EGFP (green) expression. NK1R labeled both the pFRG/RTN and 17 preBötC neurons. Magnified pFRG/RTN neurons from the caudal pole of VII (solid white rectangle in A) showing co-localization of Math1EGFP with Phox2b and NK1R. (B) shows the three markers merged. Further magnification from white boxes in B is shown to right of each panel in (B′). Image from (Rose et al 2009b).