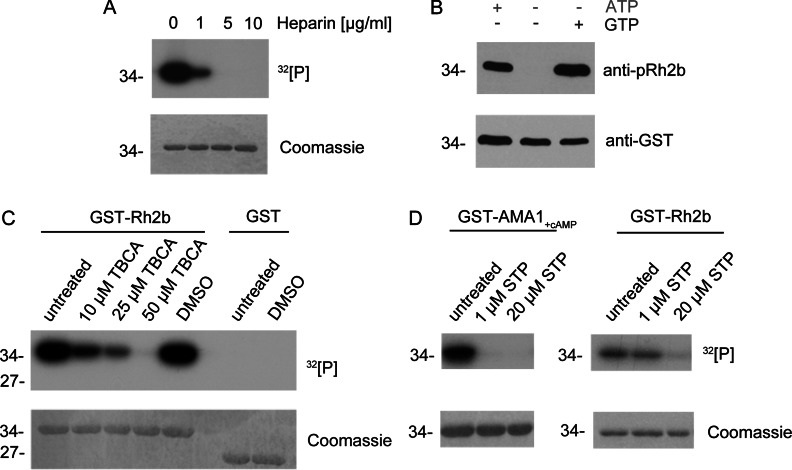
Figure 3. Inhibition of in vitro phosphorylation.
(A) Recombinant Rh2b was used in in vitro phosphorylation assays in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP with parasite lysate and different concentrations of the known CK2 inhibitor heparin. Phosphorylation as reduced by 1 μg/ml and eliminated by 5 and 10 μg/ml heparin. Upper panel, autoradiography. Lower panel, Coomassie Blue-stained SDS/PAGE. (B) The kinase, mediating Rh2b phosphorylation, was able to use ATP as well as GTP as phosphate donors. Rh2b CPD was not phosphorylated by parasite lysate in the absence of a phosphate donor. Upper panel, detection of phosphorylated Rh2b using the phospho-specific anti-pRh2b antibody. Lower panel, anti-GST antibody was used as a loading control. (C) The known CK2-specific inhibitor TBCA inhibited Rh2b CPD phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner. In presence of parasite lysate, 10 μM TBCA reduced Rh2b phosphorylation, whereas 50 μM TBCA entirely eliminated phosphorylation. The solvent (DMSO) had no effect on Rh2b phosphorylation. Upper panel, autoradiography. Lower panel, Coomassie Blue-stained SDS/PAGE. (D) Phosphorylation of Rh2b CPD by parasite lysate was resistant to staurosporine (STP) treatment. Whereas cAMP-dependent AMA1 phosphorylation was inhibited by 1 μM staurosporine, Rh2b phosphorylation was resistant and only affected by higher doses. Upper panel, autoradiography. Lower panel, Coomassie Blue-stained SDS/PAGE. The molecular mass is shown in kDa on the left-hand side of the blots.